Understanding Industrial Adhesives for Electronics Assembly
Electronics manufacturing demands precision and reliability. Every connection, component, and enclosure must withstand heat, moisture, vibration, and chemicals. Adhesive for electronics plays a vital role in sealing, bonding, and protecting delicate parts. From smartphones to industrial controls, specialist adhesives keep devices running safely and smoothly.
Key Functions: Sealing, Fixing, and Potting in Electronics
Electronic assemblies need more than just electrical connections. Adhesives serve three core functions:
- Sealing: Creating moisture and dust barriers. Prevents corrosion on circuit boards and connectors.
- Fixing (Bonding): Securing components to prevent movement during transport or operation.
- Potting/Encapsulation: Filling enclosures or coating sensitive parts. Protects against shock, vibration, chemicals, and thermal cycling.
Engineers choose adhesive types based on these needs, considering cure speed, bond strength, application method, and temperature range.
Types of Industrial Adhesives in Electronics Assembly
Adhesives for electronics come in several major chemistries. Below is a comparative table outlining key properties and common uses:
| Chemistry | Cure Process | Typical Substrates | Main Properties | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy (1K/2K) | Room/Heat | Metals, PCBs, Plastics | High strength, rigid, chemical resistant | Potting, structural bonding, gap filling |
| Industrial Silicone (RTV) | RTV/Moisture | Glass, Metals, Plastics | Flexible, high temperature, dielectric | Sealing, gasketing, vibration damping |
| Acrylic | UV/Two-Part | Plastics, Metals | Fast cure, moderate strength | Panel bonding, display modules |
| Polyurethane | Moisture/Two-Part | Plastics, Composites | Flexible, impact resistant | Encapsulating, wire tacking |
| Cyanoacrylate | Moisture/RT | Plastics, Rubber | Instant bond, brittle | Component anchoring, small fixes |
| PVA (Hot Melt/Waterborne) | Heat/Set | Papers, PCBs | Cost-effective, temporary | Reworkable masking, PCB fixturing |
Industrial Silicone RTV for Electronics
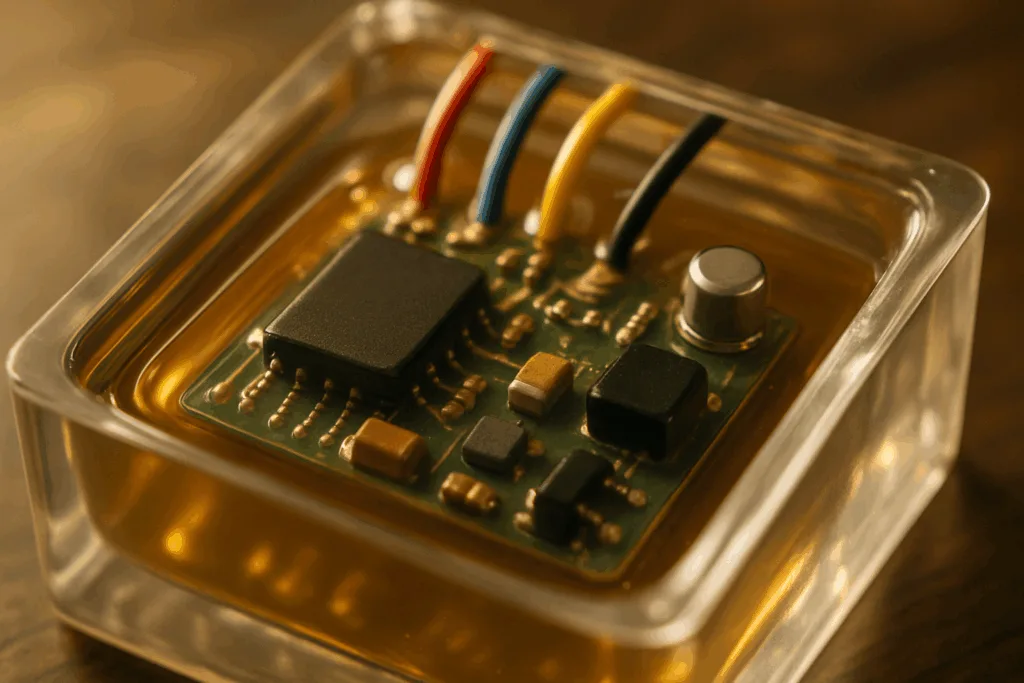
Industrial silicone adhesives, especially room-temperature vulcanizing (RTV) types, are indispensable in electronics. RTV silicones cure upon contact with air moisture, producing a flexible, rubber-like material. They bond to a wide range of substrates—glass, plastics, and metals—and maintain performance from -60°C to 200°C. These adhesives are ideal for sealing enclosures, forming gaskets on connectors, and providing dielectric insulation around high-voltage components.
RTV Silicone Properties
- One-part (1K) or Two-part (2K) systems for varied cure profiles
- Shore A hardness from 25 to 70 (soft to firm)
- Dielectric strength over 18 kV/mm
- Moisture and UV resistance
- Chemical inertness; minimal outgassing
Common RTV Applications
- Potting LED driver modules and sensors
- Sealing PCB edges and terminal covers
- Vibration damping in automotive and industrial controls
Expert Tip: Apply RTV silicone in a clean, temperature-controlled area. Cure time varies by humidity and section thickness—thicker layers may require up to 24 hours to fully solidify.
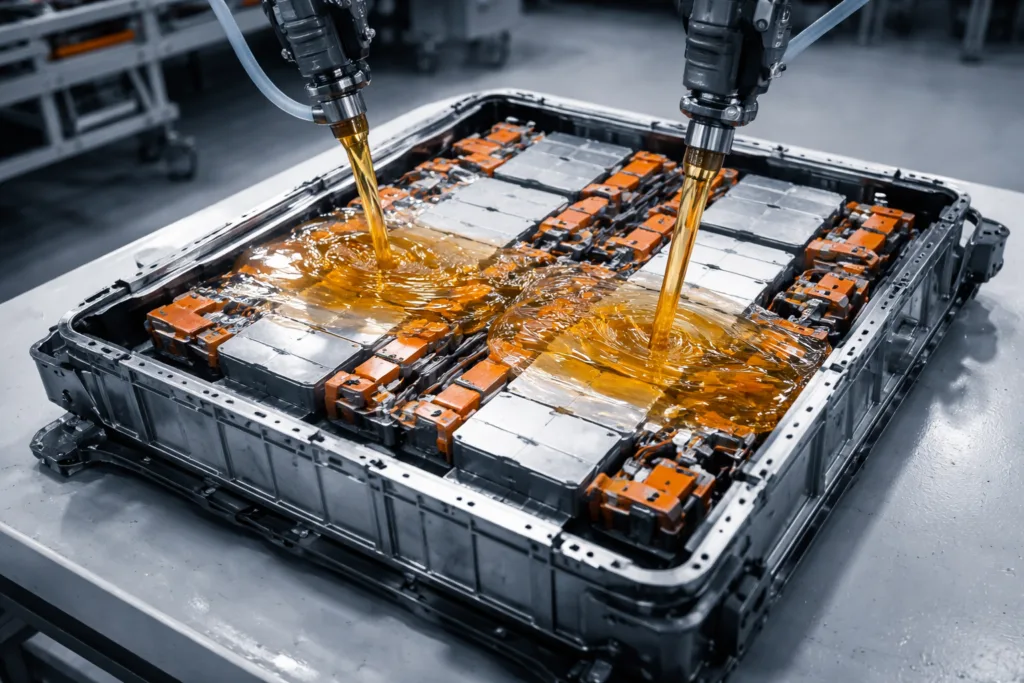
Epoxy Potting Compounds: Superior Protection
For ultimate protection, epoxy potting compounds are the go-to solution. These adhesives combine high mechanical strength with excellent chemical resistance. Once cured, epoxy forms a rigid shell that shields circuits and components from shock, vibration, water, and aggressive solvents. Epoxy systems are available in one-part (heat-curing) or two-part (room-temperature-curing) variants. Both choices can provide a tight enclosure, but two-part epoxies offer better performance in field repairs and smaller batch runs.
Epoxy Physical Characteristics
- Bond strength: Lap-shear >15 MPa (ASTM D1002 typical)
- Tensile strength up to 80 MPa
- Glass transition temperature (Tg): 80°C–180°C
- Viscosity options: 500 to >40,000 cP (customizable for potting or bead application)
Best Epoxy Adhesive Uses
- Potting transformers and inductors for protection against voltage spikes
- Fixing large electronic modules, sensors, or terminal blocks
- Gap-filling between dissimilar materials (e.g., metal to composite)
To maximize bond durability, always degrease and abrade surfaces before applying epoxy. For plastic substrates like ABS, PC, or PA, use a primer or plasma treatment for best results.
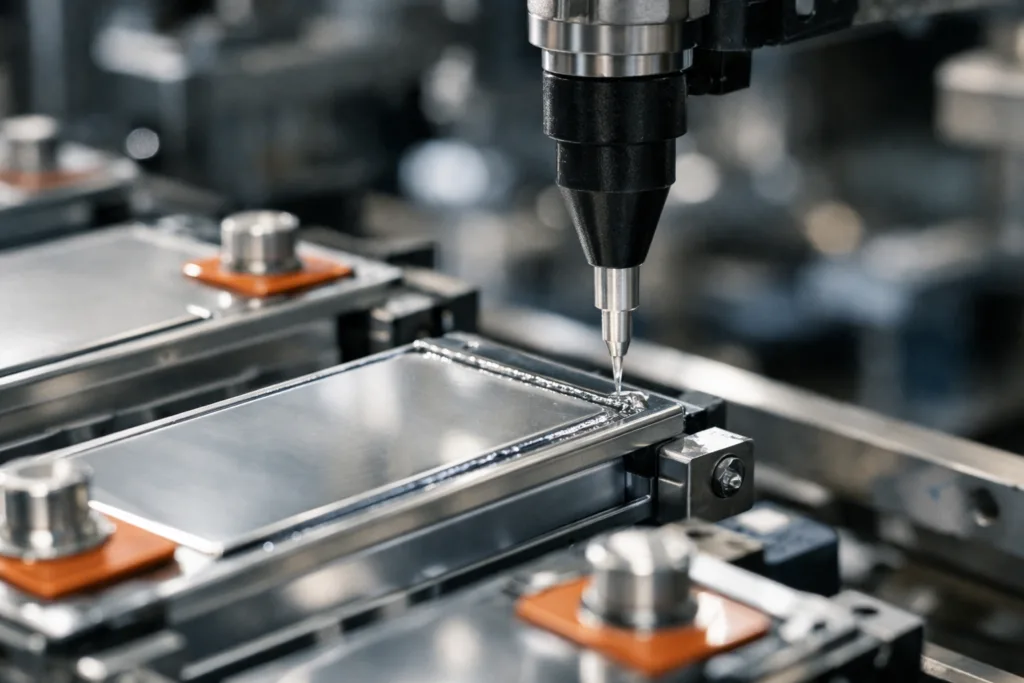
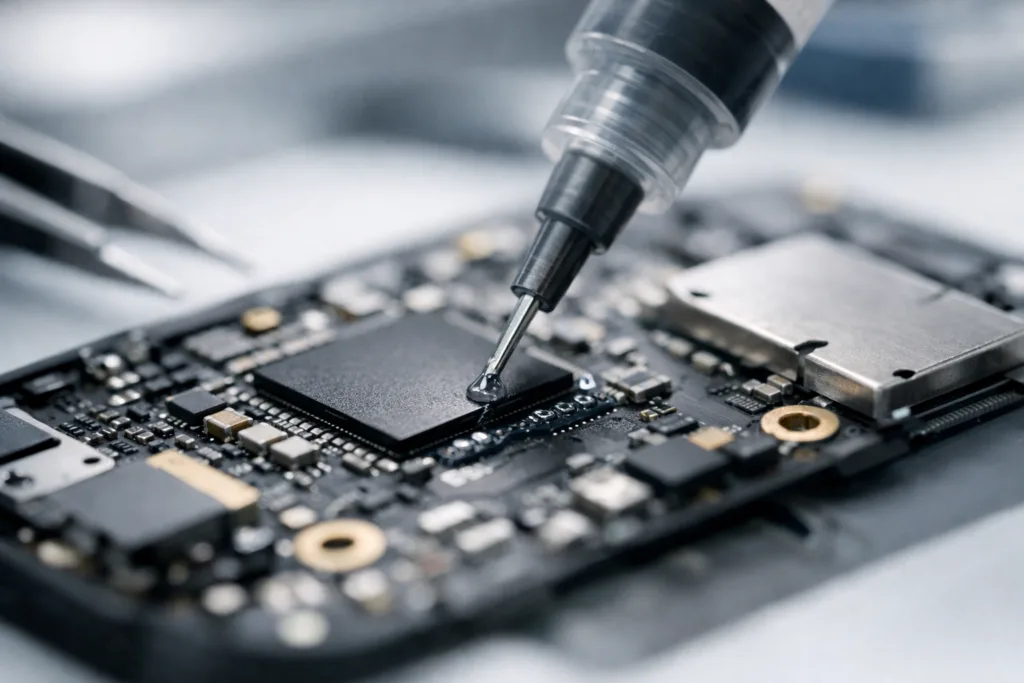
Working with PCB Adhesive: Placement & Performance
The right PCB adhesive streamlines manufacturing while improving long-term electronics robustness. PCBs are the backbone of all modern devices, and adhesives help in multiple ways:
- Surface Mount Component Attachment: Secure tiny chips or capacitors before soldering to ensure accurate placement during high-speed assembly.
- Wire Tacking: Keep wiring harnesses fixed in place, reducing strain and risk of shorts.
- Conformal Coating: Apply a thin film to protect traces from contamination and arc-over. Many coatings also use silicone or acrylic chemistries.
Performance Metrics and Standards
- Shear strength: Above 12 MPa for high-reliability designs
- Dielectric breakdown voltage per ASTM D149
- Thermal cycling resistance (from -40°C to 125°C, IEC standard)
- Compliance: REACH/RoHS/VOC-free requirements; ISO 9001 process traceability
Key Considerations When Selecting Adhesive for Electronics
Choosing the optimal adhesive for electronics depends on several factors:
- Substrate compatibility (metals, plastics, or composites)
- Operating temperature and humidity range
- Application approach (bead dispense, spray, roll-coat, or potting)
- Required cure speed (UV, heat, or room temperature)
- Mechanical requirements (flexibility vs. rigidity)
- Chemical, moisture, or salt spray exposure
For high-volume lines, cure time and viscosity can impact throughput. For mission-critical equipment, prioritize reliability and environmental ratings. Leading suppliers like ZDS offer broad selections, expert technical support, and documentation to match demanding manufacturing needs.
Automation and Quality Control in Adhesive Application
Modern factories use automated dispensers and vision inspection for precise, repeatable adhesive application. This minimizes errors and material waste, ensuring every assembly meets strict standards.
Common Process Steps
- Static mixing and controlled dispense for two-part systems
- Fixturing and clamping during cure when needed
- Temperature, humidity, and line speed monitoring
- Batch and lot tracking for quality assurance
Standards and Compliance
- Salt spray testing (ASTM B117) for corrosion resistance
- Thermal cycling, chemical soak, and accelerated aging
- Full traceable documentation for REACH, RoHS, and VOC
Industrial Adhesives for Electronics Assembly
Whether you need reliable adhesive for electronics, advanced PCB adhesive solutions, or high-performance industrial silicone, proper selection and application make the difference. ZDS delivers structural and non-structural options—from epoxies and RTV silicones to tapes and films—backed by decades supporting electronics manufacturers worldwide. Every project brings unique bonding, sealing, and potting requirements. Mastery of adhesive chemistry, cure technology, and process integration allows you to produce durable, high-quality electronic assemblies at scale.
Trends & Innovations in Electronics Adhesives
The world of electronics adhesives is advancing rapidly. UV-curable silicones now offer instant fixturing with full cure in seconds, ideal for high-speed PCB lines. Electrically conductive epoxies enable new levels of circuit miniaturization. Low-VOC and green chemistries support sustainable manufacturing goals. Smart adhesives with self-healing or thermal management properties are emerging, powering next-generation devices and electric vehicles.
Looking Ahead
Adhesive suppliers work closely with OEMs and contract electronics manufacturers to solve materials challenges early in the design phase. Whether it’s a wearable healthcare device, an EV battery pack, or an industrial sensor, the right adhesive partner unlocks greater product reliability and speed to market.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best adhesive for electronics assembly?
The best adhesive depends on your substrates, process speed, and environment. Common choices include epoxy for strength, RTV silicone for flexibility and sealing, and acrylics for fast bonding.
How is PCB adhesive applied during manufacturing?
PCB adhesive is dispensed by automated equipment, often in dots or thin lines, to secure components before soldering or to hold wires and parts during assembly.
Why use industrial silicone in electronics?
Industrial silicone provides excellent flexibility, heat stability, and dielectric properties, making it ideal for sealing, gasketing, and potting sensitive electronic components.
What is potting and why is it important?
Potting involves filling electronic modules with a resin like epoxy or silicone to shield components from moisture, vibrations, chemicals, and to prevent tampering or arcing.
How do I ensure good adhesion on plastic electronics parts?
For plastics like ABS or PC, surface preparation by degreasing and lightly abrading, or using a primer, ensures strong adhesion with most electronics adhesives.
Are electronics adhesives safe and compliant?
Reputable electronics adhesives meet global safety and environmental standards, such as REACH, RoHS, and are supplied with full SDS and quality certifications for your peace of mind.
Related Reading on Industrial Adhesives
-
- Industrial Adhesives – Applications, Materials & OEM Solutions
- Industrial Adhesives: Types, Applications, and Selection Guide
- Industrial Silicone Adhesives for Electronics & Thermal Stability
- High-Temperature Industrial Adhesives (150°C–300°C)
- Surface Preparation Techniques to Improve Adhesive Strength