Introduction to Waterproof Bonding for TWS Earbuds: Acoustic Mesh Assembly
True wireless stereo (TWS) earbuds have transformed how we experience sound on the go. Yet, with daily exposure to moisture, sweat, and environmental changes, waterproofing remains a critical design challenge. One of the most vital assembly steps is bonding the acoustic mesh—a fine barrier that protects delicate transducers while letting sound waves pass. In this guide, we’ll demystify waterproof bonding for TWS earbuds, zeroing in on acoustic mesh assembly. We’ll cover adhesive selection, surface preparation, engineering principles, and practical lessons from industry leaders.
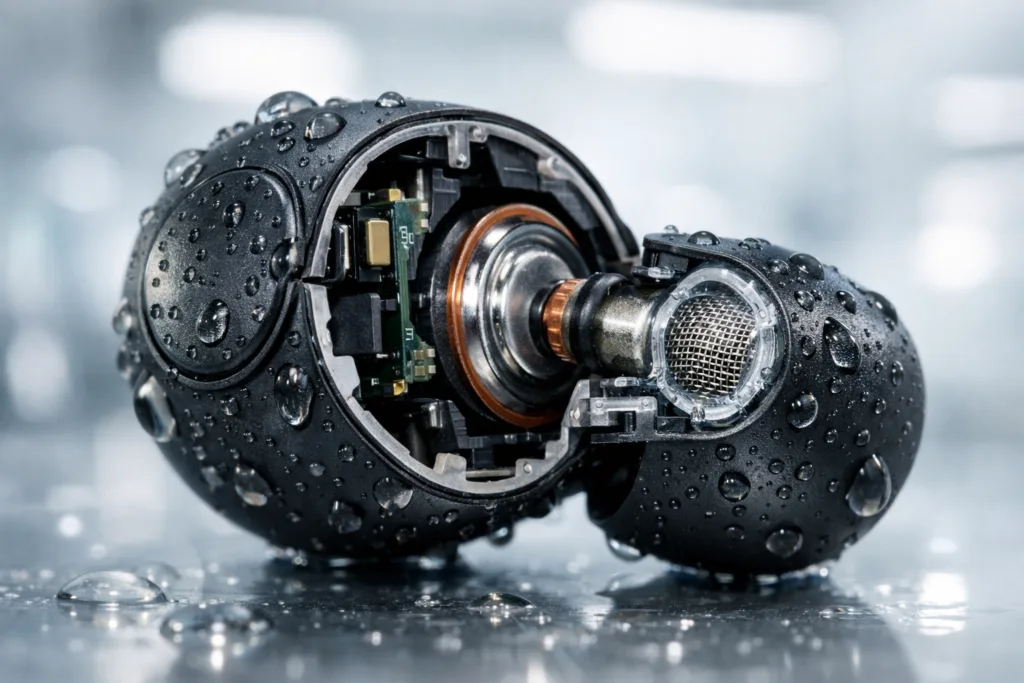
Understanding Acoustic Mesh in TWS Earbuds
The acoustic mesh is the unsung hero of TWS earbuds. It shields microspeakers and microphones from dust, water, and earwax while ensuring high-fidelity audio transmission. Typically made of hydrophobic woven polymers (like PET or nylon), this mesh requires precise bonding for reliable waterproofing without acoustic loss. Manufacturers must balance mesh porosity, thickness, and bonding method to maintain both clarity and protection.
Why Waterproof Bonding Is Essential in Earbuds
Water damage is one of the most common causes of TWS earbud failures. Waterproof bonding not only guards against incidents like accidental immersion and sweat corrosion but also extends product lifespan for regular outdoor use. High-performance bonding ensures that the mesh remains sealed to the housing, preserving sound integrity while defending sensitive electronics.
Challenges of Acoustic Mesh Assembly: A Technical Perspective
Acoustic mesh assembly faces several technical constraints:
- Bond-line must be uniform and airtight
- Adhesive must not wick into the mesh pores
- Mesh-to-plastic or mesh-to-metal interface often has low surface energy
- Process must avoid acoustic deadening or unwanted vibration
From an engineering viewpoint, success hinges on selecting the right adhesive and mastering surface preparation. For deeper dives into adhesive science, refer to resources like adhesive solutions for advanced bonding.
Material Selection: Acoustic Mesh and Housing Compatibility
Material compatibility is key. The most common mesh materials—PET, nylon, or composite fabrics—interact differently with polycarbonate, ABS, or aluminum housings. Test protocols, such as lap shear and peel strength evaluations, reveal real-world bond performance. Always review chemical compatibility charts and aging test documentation before final assembly.
Types of Adhesives for Waterproof Bonding in TWS Earbuds
In modern earbud manufacturing, adhesive choice directly affects waterproofing:
- UV-curing adhesives: Fast, precise, and suitable for temperature-sensitive substrates
- Epoxy adhesives: Provide structural strength and excellent moisture resistance
- Silicone adhesives: Offer flexibility and long-term stability, ideal for assemblies exposed to vibration
- Polyurethane adhesives: Balance toughness and elasticity for demanding environmental cycles
For detailed exploration of these adhesive families, manufacturers can refer to epoxy adhesive product specifications.
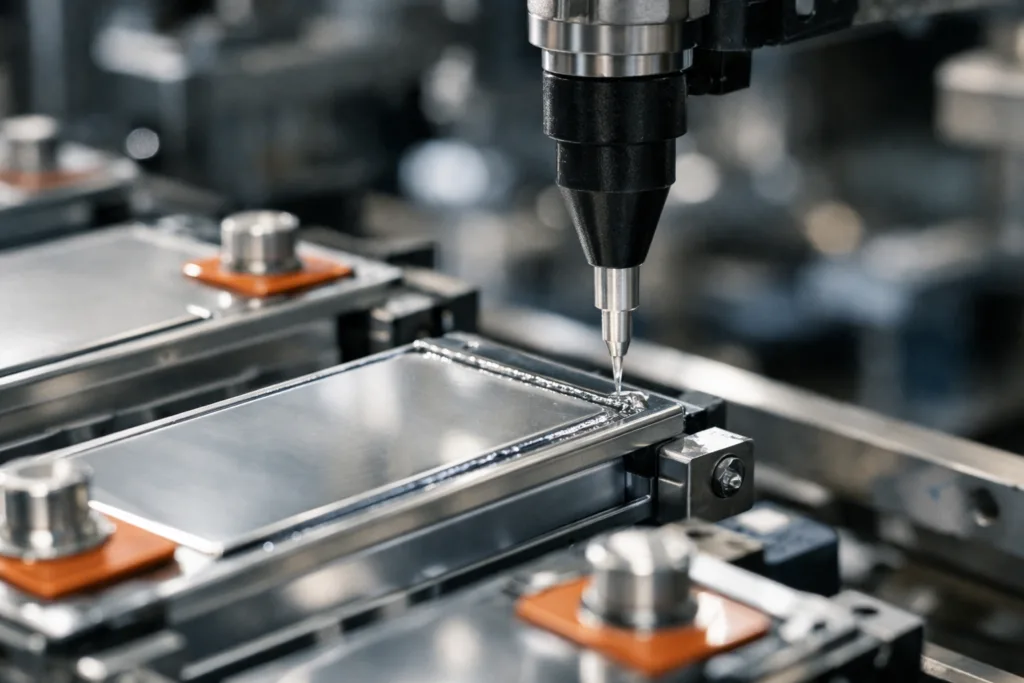
UV-Curing Adhesives: The Workhorse for Acoustic Mesh Bonding
UV-curing adhesives have become the standard for mesh assembly in TWS earbuds. They cure on demand under UV light, minimizing liquid flow into the mesh and enabling automated high-speed production. Key measurements include fixture time (under a second), bond-line thickness control (down to 0.05 mm), and consistent lap shear strength across hundreds of cycles.
Epoxy Adhesives: Offering Structural Waterproof Protection
Epoxies are prized for their robust bonding and excellent resistance to water ingress. They are often used for mesh-to-metal or mesh-to-high-temperature plastic interfaces. Set times and curing profiles can be tailored to manufacturing needs. ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, recommends adjusting epoxy formulations and cure temperatures based on housing geometry and mesh type.
Silicone and Polyurethane: Flexibility Versus Strength in Assembly
Silicone adhesives deliver lasting elasticity, which is essential if the mesh or housing flexes during use. Polyurethane offers similar resilience while also providing enhanced abrasion resistance. Both systems can be tuned for open time, viscosity, and fixture speed, though silicones tend to outperform in moisture cycling environments.
Surface Preparation for Optimal Waterproof Adhesion
Surface prep is often the deciding factor in bonding success. Proven industrial protocols include:
- Plasma or corona treatment to raise surface energy
- Solvent cleaning to remove oils and mold residues
- Mechanical abrasion for roughening
Reviewing thorough surface preparation techniques improves bond reliability and cycle time.
Application Techniques: Ensuring a Precise Bond-Line
Bond-line uniformity is non-negotiable for acoustic meshes. Automated micro-dispensing robots, needle valves, and laser-guided placement ensure repeatable results. High-speed camera monitoring in production helps avoid overapplication (which can block mesh pores) or underapplication (leading to leaks).
Process Controls in Acoustic Mesh Assembly
Critical process variables to monitor include:
- Ambient humidity and temperature
- Adhesive pot life and open time
- UV intensity and cure uniformity
- Housing/mesh alignment tolerances
Quality assurance programs should include destructive and non-destructive leak tests, acoustic transmission checks, and environmental aging simulations.
Engineering Best Practices for Durability and Waterproofing
Real-world manufacturing lessons show that best practices—such as verifying adhesive cure profiles, monitoring assembly pressure, and periodic requalification of mesh inventory—lead to fewer customer returns. Work-ins such as automated visual inspection limit assembly drift and ensure ongoing waterproof reliability.
Preserving Acoustic Performance: Avoiding Blockage and Damping
The adhesive must protect without interfering with sound transmission. Overfill or wicking into mesh pores can dampen treble or muffle voice pickup. Optimized adhesive viscosity (low enough to stay on the bond-line, thick enough to avoid mesh penetration) and controlled cure rates prevent these issues.
Industry Case Studies: Successful Waterproof Mesh Assemblies
Case studies reveal practical insights. A leading consumer audio brand reduced warranty claims by 40% after switching to a dual-cure UV epoxy system tailored for nylon mesh. Another OEM extended earbud IP rating (Ingress Protection) from IPX4 to IPX7 by integrating both plasma-treated mesh and high-lap shear UV adhesives. These improvements stemmed from test-based design, cross-department troubleshooting, and ongoing process audits.
Common Failures in Waterproof Bonding and How to Prevent Them
Industry data shows recurring issues like:
- Poor surface cleaning, causing adhesive lift-off
- Excess adhesive, blocking acoustic mesh
- Incompatible adhesive/mesh interface, resulting in delamination
Proactive measures, such as integrating pre-bond mesh inspections and maintaining consistent humidity control, minimize these risks. For more troubleshooting guidance, see how to avoid common industrial adhesive failures.
Optimizing Waterproof Adhesive Performance in TWS Earbuds
Controlling key variables—adhesive viscosity, bond-line pressure, cure time, and post-cure aging—delivers repeatable results in mass production. Advanced monitoring (infrared, ultrasonic) in assembly lines identifies weak bonds before shipment. Regular audits and data logging build process stability and high IP ratings for demanding markets.
Environmental and Regulatory Standards for Waterproof Bonding
Global standards such as IPX4, IPX7 (IEC 60529) guide waterproof requirements. RoHS and REACH compliance for adhesive chemicals ensures environmental safety. Documentation for acoustic transmission and waterproofing must accompany each production batch in quality-controlled environments.
Waterproof Bonding for TWS Earbuds: Acoustic Mesh Assembly
This section brings together everything we’ve covered. Waterproof bonding for TWS earbuds—especially acoustic mesh assembly—is a multi-step operation requiring adhesive expertise, precision engineering, and process vigilance. Prioritizing material compatibility, application control, and real-world test data yields reliable acoustics and durable waterproofing. When in doubt, cross-reference industry guides and consult process engineers for tailored solutions.
Future Innovations in Waterproof Mesh Bonding
By 2026, nano-engineered meshes and smart adhesives with self-healing properties are stepping into production. These advances promise enhanced IP ratings, longer earbud lifespans, and simpler recycling of wearable electronics. AI-driven monitoring is already reducing defect rates and enabling predictive quality control in acoustic mesh assembly.
ZDS Adhesive Insights: Application-First Assembly Rules
From an assembly-line viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, the most effective waterproof bonding for TWS earbuds involves step-wise surface activation, adhesive selection based on housing/mesh material, and ongoing bond integrity testing. For PET mesh bonded to PC housing, a UV-curable structural adhesive with a fixture time ≤ 5 seconds has consistently passed thermal cycling and humidity aging. Parameters such as bond-line thickness (≤ 0.07 mm), adhesive open time (≤ 30 seconds), and moisture resistance (IPX7) are core to process validation. Maintaining documentation is just as vital as production itself.
Summary Table: Comparing Adhesives for Acoustic Mesh Assembly in TWS Earbuds
| Adhesive Type | Cure Mechanism | Moisture Resistance | Acoustic Impact | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UV-curing | Light-activated | Excellent | Minimal | Fast automated mesh bonding |
| Epoxy | Heat/room temp | Excellent | Low to moderate | Structural mesh-housing bonds |
| Silicone | Condensation/catalyst | Good | Minimal | Flexible mesh interfaces |
| Polyurethane | Moisture/catalyst | Good-Excellent | Low | Vibration-prone assemblies |
Conclusion: Raising Standards in TWS Earbud Waterproof Bonding
Waterproof bonding for TWS earbuds—particularly at the acoustic mesh—blends precision engineering, materials science, and strict process control. By focusing on adhesive choice, rigorous surface preparation, and vigilant assembly practices, manufacturers can elevate durability and acoustic performance, reducing failures and strengthening brand reputation. In the evolving world of wearable tech, this expertise is the foundation of next-generation products.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the function of the acoustic mesh in TWS earbuds?
The acoustic mesh protects the internal components from moisture and debris while ensuring clear sound transmission.
Which adhesive types are best for waterproof mesh assembly?
UV-curing, epoxy, silicone, and polyurethane adhesives are the most widely used for mesh bonding with waterproof requirements.
How can manufacturers prevent acoustic loss during bonding?
Controlling adhesive quantity and viscosity, and using precise application tools, helps prevent mesh blockage and preserves sound clarity.
What tests ensure bonded mesh waterproof durability?
Common tests include leak detection, lap shear, peel strength, humidity aging, and acoustic transmission monitoring.
Is surface preparation necessary for bonding acoustic mesh?
Yes, cleaning and activating the surface is vital for strong, reliable, and waterproof adhesive bonds.
How does the assembly process maintain IPX ratings?
Following standardized adhesive workflows, verifying bond integrity, and documenting all test results help maintain and certify IPX waterproof ratings.
Related Reading
- Discover Performance Trends for UV Glue in Electronics Assembly
- Avoid Critical Industrial Adhesive Failures: Field-Proven Strategies
- UV Curing Adhesive Breakthroughs for Modern Electronics
- Advanced Adhesive Solutions for Renewable Energy Applications
- Step-by-Step Guide: Choose the Right Industrial Adhesive Every Time