Introduction: Exploring B-Stage Epoxy and Its Industrial Value
B-Stage Epoxy: Applications, Storage, and Processing is a cutting-edge topic in materials engineering, with wider relevance for electronics, construction, and automotive sectors in 2026. B-stage epoxy is a partially cured adhesive, offering the flexibility to pause production before final bonding, making it a sought-after solution in assemblies where precision and efficiency matter. This guide explains B-stage epoxy’s unique properties, optimal storage strategies, and step-by-step processing techniques, supporting users from first selection through practical application.
What is B-Stage Epoxy?
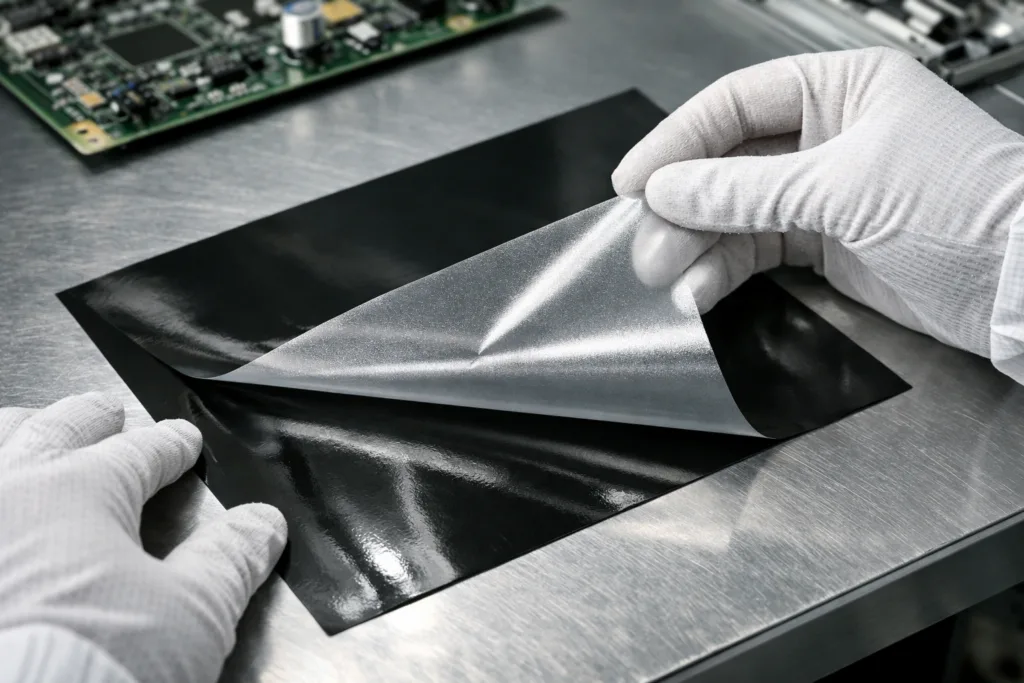
B-stage epoxy is an adhesive formulation cured to a midway point—between liquid (A-stage) and fully cured (C-stage)—where it is solid but still reactive. Its ability to be handled, repositioned, and stored before final cure sets it apart from conventional adhesives, especially for complex assemblies.
Key Properties of B-Stage Epoxy
B-stage epoxy has a partially polymerized structure, which provides several manufacturing advantages:
- Thermal stability: Resists premature curing below target temperature
- Handling strength: Parts can be manipulated without adhesive failure
- Extended shelf-life: Stays viable until intentionally activated
- Controlled processing: Final cure is scheduled for optimal cycle time
Why Choose B-Stage Epoxy?
Compared to traditional A-stage or C-stage adhesives, B-stage epoxies bridge workflow gaps for manufacturers needing both placement flexibility and high-strength bonds. For assemblies requiring clean handling, precise pre-placement, or large-batch scheduling, B-stage is a clear winner.
Main Applications of B-Stage Epoxy
B-stage epoxy’s adaptability makes it ideal in several high-value industries:
- Printed circuit board (PCB) assembly
- Semiconductor packaging
- Automotive body-in-white and glass bonding
- Construction panels and composite laminates
- Wind turbines, battery packs, and sensors
For a deeper dive into industrial use, explore the epoxy adhesive product page which showcases advanced options for electronics and automotive industry needs.
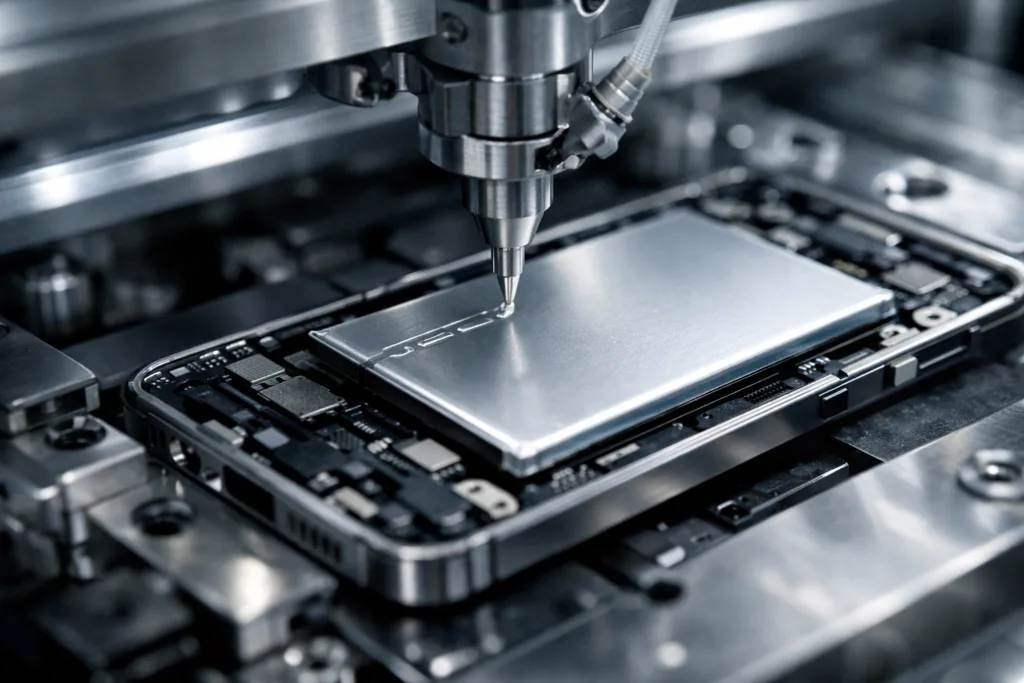
B-Stage Epoxy in Electronics: Benefits and Techniques
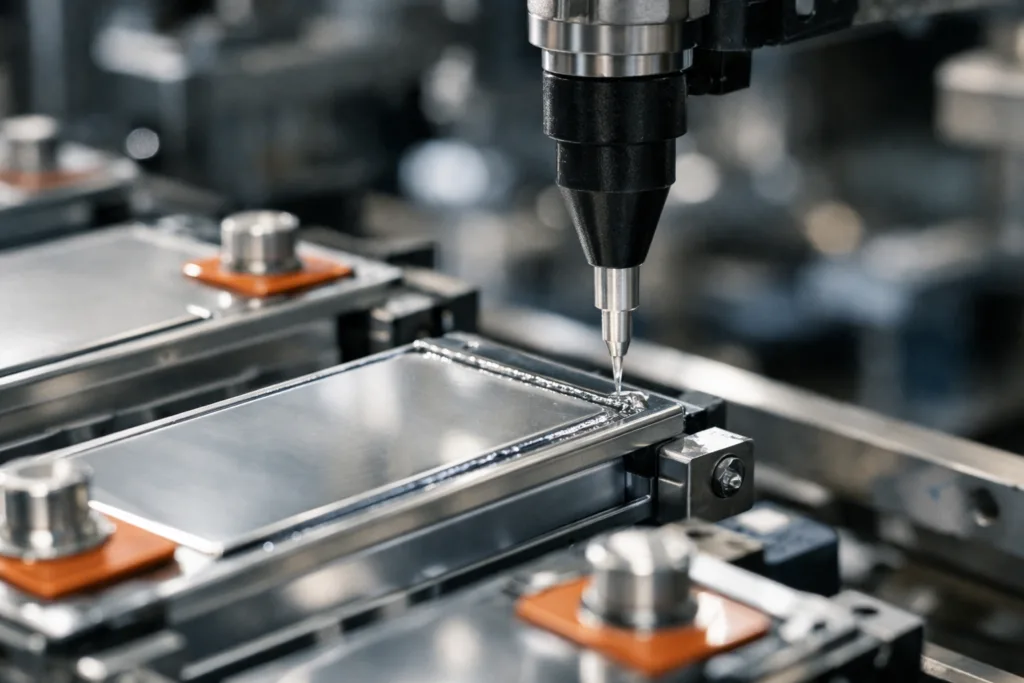
In electronic manufacturing, B-stage epoxies enable high-speed alignment and multilayer lamination without voids or misplacement. Their controlled latencies suit high-density surface-mount technology and fine-pitch device bonding.
Construction Uses: Strength, Stability, and Scheduling
B-stage epoxy is leveraged in construction panels and precast members, where manufacturing timelines demand flexible adhesive application and assurance against premature curing. Architects and engineers rely on it for modular builds and thermal insulation sandwich panels.
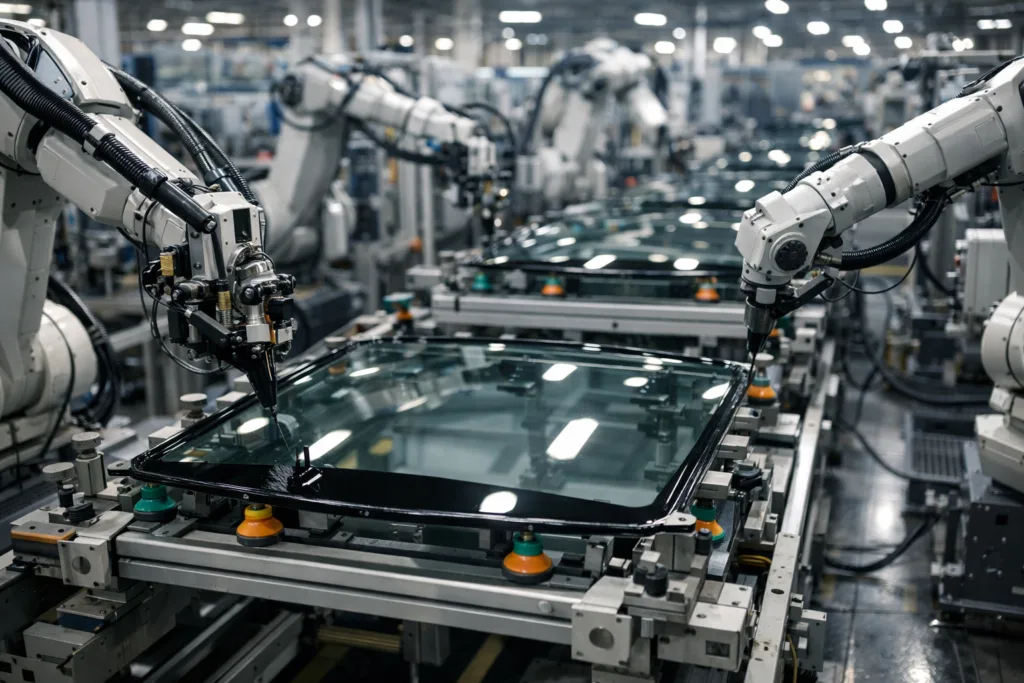
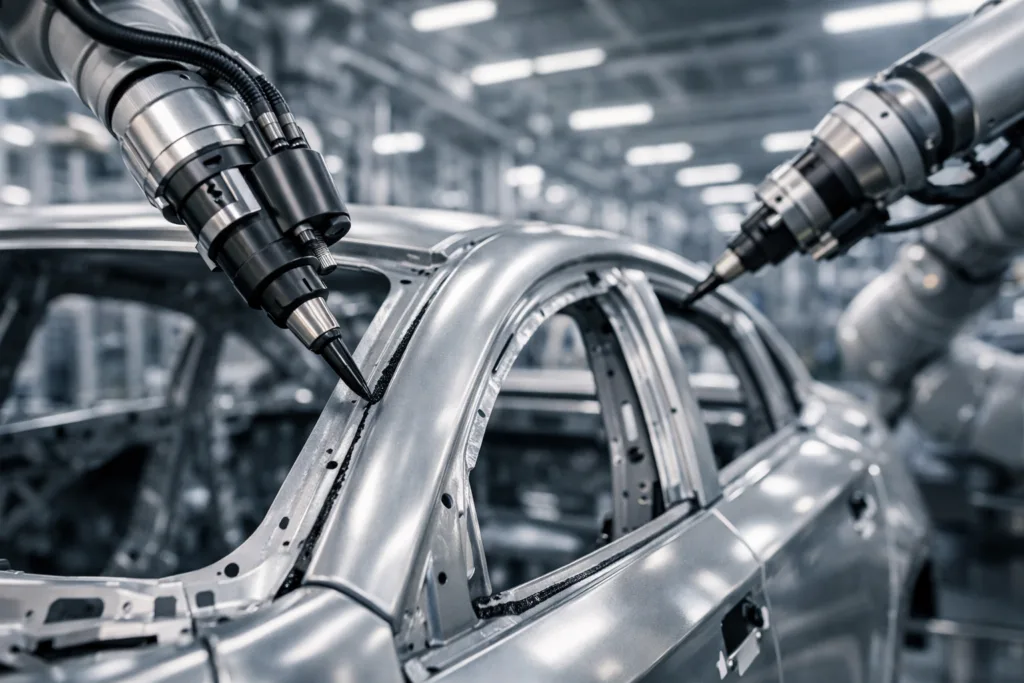
Automotive Industry: Safety, Throughput, and Advanced Adhesive Systems
Modern automotive assembly lines use B-stage epoxy in glass installation and body sheet bonding, improving throughput and fixture control. ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, applies B-stage technology in automotive weatherstrip, mirror, and glass adhesive solutions to enhance cyclic durability under temperature and vibration.
Interested in automotive-specific adhesives? See the automotive adhesive manufacturer guide for further technical details.
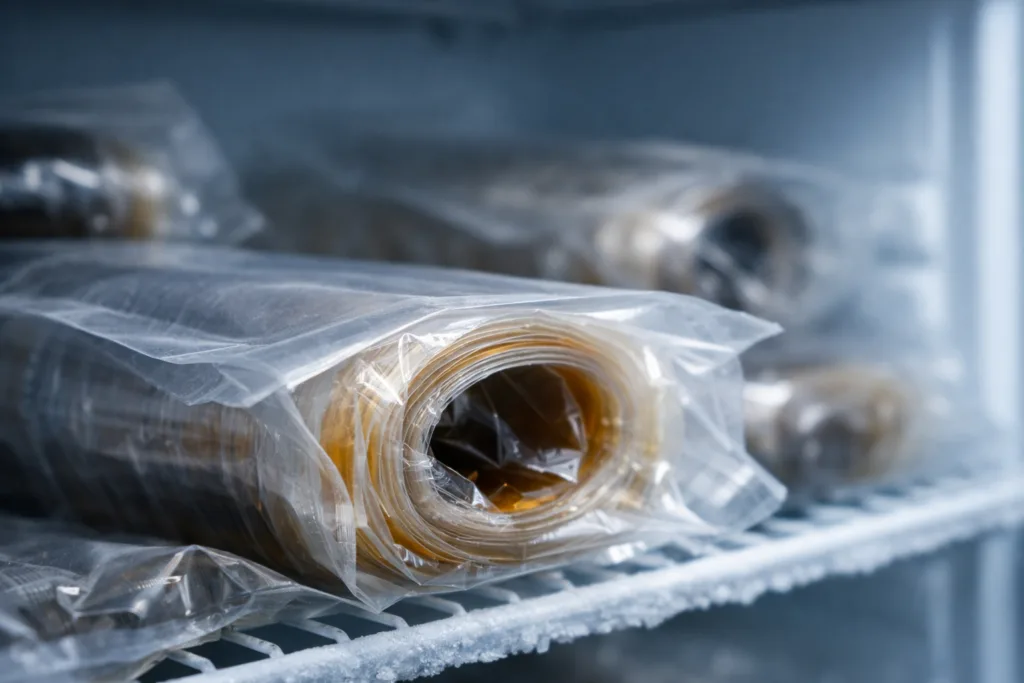
Optimal Storage Conditions for B-Stage Epoxy
Maintaining B-stage epoxy’s reactivity and handling strength calls for strict storage controls. Key parameters include:
- Temperature: 2–8°C (refrigerated), to minimize premature cure
- Humidity: Below 50% RH, preventing moisture-triggered activation
B-stage materials should be kept in airtight containers away from direct sunlight and thermal cycling. Logistic planners should account for “first in, first out” (FIFO) usage and monitor expiration dates as provided by the adhesive manufacturer.
Packaging Forms and Handling Tips
B-stage epoxy is typically supplied as preforms, films, or pellets. Each form demands careful handling:
- Minimize out-of-freezer exposure; only open immediately before use
- Allow temperature equilibration to avoid condensation
- Avoid flexing/scratching adhesive surfaces during layup
For more advanced packaging knowledge, visit the industrial adhesives reference for film-backed and specialty processing solutions.
Processing Stages of B-Stage Epoxy: From Pre-Cure to Final Cure
The value of B-stage epoxy is unlocked through its processing flexibility. Here are the main phases:
- Pre-Cure (B-Stage): Material reaches a tack-free, solid state for handling
- Placement: Layup, alignment, or bulk packing completed without the need for rush
- Final Cure (C-Stage): Heat, UV, or pressure is applied for complete polymerization
Curing Techniques: Thermal, UV, and Pressure Approaches
Depending on formulation, B-stage epoxies may require one or more activation techniques:
- Oven bake: 120–180°C for 30–90 minutes
- Autoclave: Elevated temperature and pressure cycles
- Infrared/UV exposure: Suitable for thin films
Monitoring both time and temperature profiles is vital. Incorrect curing can cause incomplete bonds, void formation, or compromised mechanical strength.
Performance Implications in End-Use Applications
Properly cured B-stage epoxy delivers predictable lap shear strength, peel resistance, and electrical insulation. Its reliable bond-line thickness and minimal shrinkage ensure part integrity and dimensional stability under load, vibration, and temperature extremes.
Comparing B-Stage Epoxy to Other Structural Adhesives
| Property | B-Stage Epoxy | One-Part Epoxy | UV Adhesive |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handling Time | Long | Short | Very Short |
| Fixture Strength | Medium | Low | Varies |
| Cure Scheduling | Flexible | Fixed | Instant |
| Application Range | High | Medium | Medium |
Key Quality Control and Testing Methods
- Lap shear testing: Measures joint strength under tension
- Peel testing: Evaluates bond resistance to separation
- Thermal cycling: Assesses stability under repeated heating/cooling
- Humidity exposure: Detects moisture-related elastic changes
Common B-Stage Epoxy Failure Modes and Prevention
If B-stage epoxy is not stored or processed correctly, users may face:
- Premature curing and poor positionability
- Surface contamination or film delamination
- Void formation due to trapped moisture or air
- Reduced mechanical performance
Routine audits of storage logs, batch testing, and cleanroom practices go a long way to avoiding these pitfalls.
Sustainability and Repairability Considerations in 2026
B-stage epoxy offers optimized yield and scrap rates, contributing to greener manufacturing processes. Its delayed cure properties help minimize waste from positioning errors, reducing rework and landfill impact, which matters more than ever in today’s eco-aware assembly landscape.
Future Trends: Formulation, Fillers, and Automation
Modern B-stage epoxies incorporate nano-fillers for improved thermal conductivity, and smarter automation controls are making sequential layup and mass-processing more accessible for mid-sized manufacturers. The trend favors faster, lower-energy cures and tunable performance for specialty purposes.
Practical Decision Checklist: Is B-Stage Epoxy Right for Your Project?
- Does the assembly require delayed bonding during production?
- Do you need a balance between handling time and rapid final strength?
- Is temperature cycling anticipated in end-use?
- Will parts need repositioning, repair, or bulk storage before final cure?
- Is high mechanical strength or electrical insulation needed?
Expert Insights: In-Process Observations from Assembly Lines
From an assembly-line viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, consistent humidity, part cleanliness, and scheduled removal from cold storage are critical for repeatable B-stage results. (Ideal open time: 30–60 minutes at ambient, fixture time post-cure: 5–20 minutes depending on substrate.) Cross-link density increases sharply in final cure, so tight controls on ramp-up temperature yield maximum bond strength.
B-Stage Epoxy: Applications, Storage, and Processing
B-stage epoxy continues to stand out in 2026 for its versatility, ease of scheduling, and robust physical properties, suiting projects in electronics, construction, and automotive industries. Careful storage (refrigerated, low humidity), precise processing (timed curing, tested parameters), and proper quality controls ensure the benefits of B-stage formulation are fully realized in modern manufacturing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What distinguishes B-stage epoxy from typical adhesives?
B-stage epoxy is partially cured, making it solid yet still reactive, ideal for flexible positioning and batch processing before final cure.
What are the optimal storage conditions for B-stage epoxy?
Store B-stage epoxy at 2–8°C in airtight containers, with relative humidity below 50% to prevent premature curing or moisture activation.
Which industries benefit most from B-stage epoxy?
Electronics assembly, automotive manufacturing, and construction panels benefit greatly due to the ability to delay curing and enable complex assemblies.
How is final curing performed for B-stage epoxy?
Final curing typically involves controlled heating (oven or autoclave), sometimes combined with pressure or infrared/UV exposure, depending on the application.
What are common failure modes with B-stage epoxy?
Common issues include premature curing, position errors, film contamination, and voids; these are best avoided with strict storage and process controls.
Can B-stage epoxy improve the sustainability of manufacturing?
Yes, B-stage epoxy reduces material waste, enables rework of misaligned parts, and optimizes yield, contributing to greener assembly processes.