Polyurethane Industrial Adhesives: Best Use Cases
Polyurethane (PU) industrial adhesive offers a unique balance of flexibility, strength, and durability, making it ideal for bonding a wide range of materials—especially where vibration resistance and toughness matter. Industries such as automotive, furniture, and construction rely on polyurethane bonding to join surfaces that must withstand movement, shocks, and harsh conditions.
Understanding Polyurethane Chemistry: Why It Works
Polyurethane adhesives have a special chemical structure. They contain hard and soft segments, which allow them to flex, absorb stress, and maintain high bonding strength. Most PU adhesives cure by reacting with moisture (moisture-cure), though some use heat or two-part systems for faster setups. Their ability to crosslink during cure delivers bonds that resist vibration and expansion without cracking.
Key Polyurethane Adhesive Formulations
- 1K moisture-cure PU: Single-component, easy to apply, cures with ambient humidity. Used in construction and laminating.
- 2K polyurethane: Two-part system, fast curing, controlled mixing for strong bonds. Common in automotive and industrial assembly.
- Hot-melt PU: Thermoplastic, reheatable, and easy for automated dispensing. Used frequently for wood, furniture, and door panels.
Cure Properties and Performance
Typical PU adhesives offer working times of 5–30 minutes and reach handling strength in about an hour. Final cure usually takes 24 hours, depending on humidity, temperature, and substrate. Shore A or D hardness varies with formulation; softer grades promote flexibility, while higher durometer types provide rigid bonds. Viscosity ranges from thin liquids (100–500 cP) for spraying, to paste-like (5,000–30,000 cP) for gap filling.
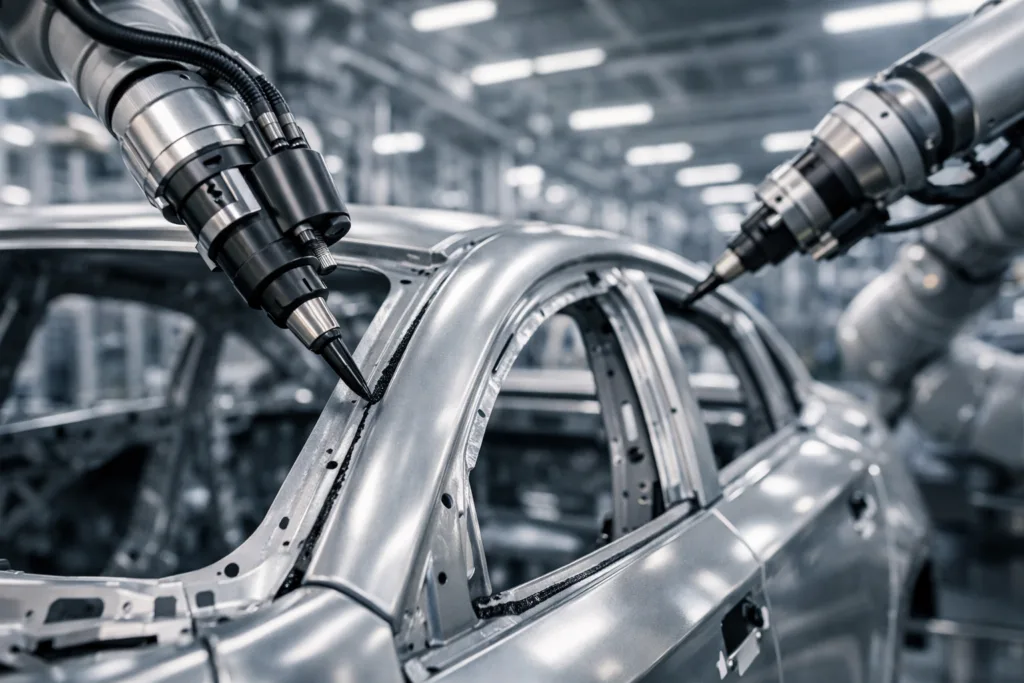
Automotive Interiors: Polyurethane Bonding Applications
Vehicle interiors demand adhesives that tolerate thermal cycling, vibration, and complex material combinations. PU industrial adhesive excels here by firmly bonding plastics (ABS, PC, PP), synthetic leather, foam, and fabrics. Polyurethane’s inherent flexibility prevents cracking when door panels and trim experience repeated shocks and movements during driving.
Best Practices in Car Interior Assembly
- Prepare surfaces: Clean, degrease, and roughen plastics for optimal adhesion.
- Apply even beads or dots with slot-die or bead dispensers; static mixers ensure 2K blends.
- Clamp assemblies for at least 30 minutes if possible, until handling strength develops.
- Verify with lap-shear (ASTM D1002) and T-peel (ASTM D1876) tests for quality assurance.
Vibration Resistance and Safety
PU adhesives deliver lap-shear strength of 5–11 MPa with excellent T-peel results. Tests under vibration and thermal cycling confirm strong bonds without brittle failure, meeting automotive standards for safety and comfort. ZDS offers tailored PU adhesives for car interiors to match worldwide OEM specifications.
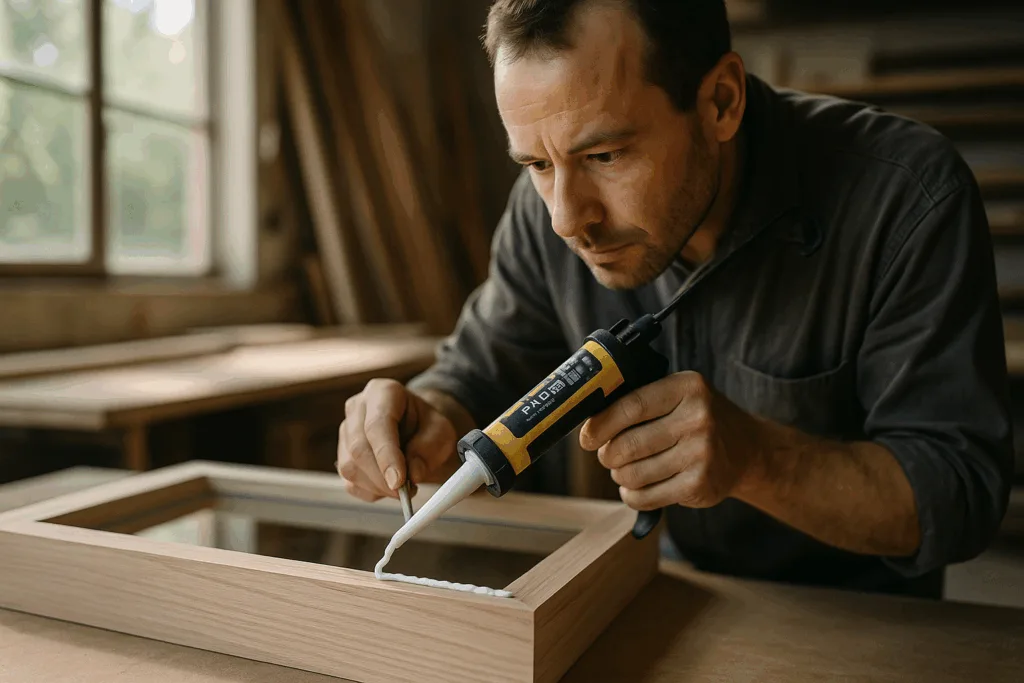
Wood Bonding: Polyurethane for Furniture and Construction
Wood joins benefit from polyurethane’s gap-filling capability and ability to flex with natural material movement. PU industrial adhesives bond pine, hardwood, MDF, and engineered panels, resisting splits and warping due to changes in humidity and temperature. This makes them a top choice for doors, parquet floors, and custom furniture.
Common Applications and Advantages
- Parquet flooring: PU adhesives absorb slight expansion and contraction, reducing squeaks.
- Door assembly: Bonds wood to glass inserts, or metals, with shock resistance.
- Custom joinery: Fills gaps, hides imperfections, and delivers fast setups for craftsmen.
Expert Insight
ZDS recommends moisture-cure PU for wood, as it delivers strong initial tack and gap filling within minutes—crucial for fast production lines.
Plastic Bonding: Polyurethane Advantages for Engineering Polymers
Bonding plastics requires an adhesive that sticks despite low surface energy and flexibility. Polyurethane adhesives bond ABS, PC, PET, PA, and rigid vinyl with ease. Some plastics benefit from surface treatment (corona, plasma, or primers) to maximize bond strength. PU delivers elongation up to 300%, so joints handle stretch and vibration without stress-induced cracks.
Design Tips for Plastic Bonding
- Use primers for polypropylene and polyethylene to promote adhesion.
- Choose flexible PU grades for assemblies exposed to shock or frequent movement.
- Spray or bead application by automated robot or hand dispenser ensures uniform coverage.
Chemical and Thermal Resistance
PU adhesives withstand chemicals such as oils, mild acids, and cleaning agents. They maintain strength from -40°C to 90°C, making them reliable for consumer electronics, appliances, and automotive parts.
Comparative Table: PU Chemistry vs. Bonds & Applications
| PU Chemistry | Supported Substrates | Key Properties | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1K Moisture-Cure | Wood, plastics, stone, metals | Flexible, gap-filling, moderate tack | Flooring, construction, furniture |
| 2K PU | Metals, composites, plastics | Fast cure, high strength, adjustable viscosity | Automotive interiors, industrial assembly |
| Hot-Melt PU | Textiles, wood, foam, plastics | Reheatable, sprayable, quick setup | Door panels, upholstery, lamination |
Multi-Material Bonding: Why Polyurethane Leads
Designers often need adhesives that link different materials—plastic to metal, wood to stone, or foam to textile. PU industrial adhesive shines because it adjusts to expansion rates, smooths over flaws, and resists shocks. Flexible grades handle vibration-prone assemblies such as machinery panels, consumer electronics, and wall claddings.
Substrate Preparation and Adhesion Promoters
- Degrease all surfaces to remove oils.
- Abrade with sanding or grit-blasting for rough textures.
- Apply adhesion promoters for metals and engineered plastics.
Process Automation and Quality Control
- Robotic bead, slot-die, or spray dispensing ensure repeatable coverage.
- Use QC tests: lap-shear, salt spray (ASTM B117), and thermal cycling for long-term durability.
- Comply with REACH/RoHS and VOC regulations; maintain lot traceability for confidence.
Vibration Resistance and Flexibility: Key Performance Benefits
Many industrial assemblies face shocks, vibrations, and movement—especially in vehicles and heavy equipment. PU adhesives flex with joined materials, preventing joint fatigue and micro-cracking. They maintain bond strength over hundreds of vibration cycles. In floor and wall systems, PU provides acoustic dampening, improving comfort while withstanding repeated loads.
Testing for Strength and Durability
- Lap-shear (ASTM D1002): measures bond strength up to 11 MPa.
- T-peel (ASTM D1876): shows high peel resistance for layered panels.
- Thermal cycling: ensures stability over temperature fluctuations.
Special Applications: Stone, Foam, Glass, and Hybrid Substrates
PU adhesives serve specialty bonding needs beyond common wood and plastics. They adhere to stone in flooring, foam in insulation panels, and glass in display units. Flexible grades allow for expansion and contraction, reducing stress concentrations. For hybrid materials, such as composite decking or decorative panels, PU maintains cohesive bonds despite different expansion rates.
Stone and Flooring Applications
- Bond granite or marble tiles with moisture-cure PU for vibration damping.
- Install insulation foam boards using sprayable PU for fast coverage.
Glass and Transparent Plastics
ZDS offers UV-stable PU adhesives for glass-to-metal or glass-to-plastic bonds, ensuring clarity and strength over years of service.
How to Choose the Right PU Industrial Adhesive
Selecting the best PU adhesive depends on the substrate, environmental demands, and application process. For automotive interiors and moving assemblies, flexible grades (elongation 200–300%) resist breakage. Harder grades suit cabinetmaking, flooring, and rigid panels. Always check cure speed (pot life, open time), gap-filling ability, and end-use strength.
Checklist for PU Adhesive Selection
- Check substrate compatibility and surface prep requirements.
- Review cure speed versus process times.
- Consider flexibility vs. rigidity needed in the final joint.
- Look for compliance certifications: REACH, RoHS, VOC, ISO 9001.
- Ask ZDS for guidance—custom formulations support global manufacturing standards.
Storage, Handling, and Compliance Tips
Polyurethane adhesives should be stored in sealed containers at 10–25°C to prevent pre-cure. Moisture-cure products must avoid high humidity until applied. Use SDS for safety and train operators to avoid skin contact and inhalation of vapors. Compliance with REACH/RoHS and proper documentation ensures safe handling across markets.
Quality Assurance Measures
- Inspect each lot for viscosity and cure speed.
- Test bonds with salt spray, thermal cycling, and aging studies.
- Maintain full documentation for traceability and audits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes PU industrial adhesive ideal for multi-material bonding?
PU adhesives flex with different materials, absorb vibration, and fill gaps, making them perfect for joining plastics, wood, metal, and composites.
How do you prepare surfaces for strong polyurethane bonding?
Clean, degrease, and roughen surfaces; use adhesion promoters or primers for tough plastics or metals to get the best bond strength.
What cure speed can be expected with polyurethane adhesives?
Most PU adhesives reach handling strength in 30–60 minutes and fully cure in 24 hours, depending on temperature, humidity, and formulation.
Are polyurethane adhesives safe for automotive interiors?
Yes, PU adhesives meet automotive standards for vibration resistance, temperature stability, and VOC regulations, making them safe and durable for interiors.
Can PU adhesives bond stone, foam, or glass?
PU adhesives work on stone, foam, and glass, especially when pairing flexible grades and using proper surface prep for clean, lasting bonds.
How does ZDS support custom polyurethane adhesive solutions?
ZDS provides tailored PU adhesive formulations that match industry specifications, substrate needs, and global compliance for reliable manufacturing.