Introduction to Thermal Runaway and Fire-Retardant (UL94 V-0) Solutions
Thermal runaway is one of the most concerning risks in battery-powered devices and electronics today. When unchecked, it can lead to dangerous fires or explosions, making prevention vital for manufacturers and users alike. Fire-retardant materials certified as UL94 V-0 are now the gold standard for controlling thermal runaway, thanks to their ability to prevent the spread of fire. This article explores the science behind thermal runaway, how UL94 V-0 materials are integrated to mitigate these hazards, and how various industries are adopting these advancements for safer electronics.
What is Thermal Runaway?
Thermal runaway describes a scenario where increasing temperatures cause a feedback loop that drives even higher temperatures—often reaching a point where components catch fire or explode. In battery systems, this is typically triggered by excessive charge, short circuits, or physical damage, which cause internal temperatures to rise rapidly.
The Chemistry of Heat Generation Inside Batteries
Internal battery reactions, like electrolyte decomposition and electrode breakdown, release energy as heat. If this heat isn’t managed, it can accelerate reactions, raising temperatures further. This cycle—called exothermic reaction—quickly reaches dangerous levels in poorly protected designs.
Why Thermal Runaway is Critical in Modern Electronics
Today’s electronics are smaller, faster, and packed with higher-capacity rechargeable cells. While performance has soared, so has the risk. For example, electric vehicles (EVs) and laptops use tightly packed lithium-ion batteries that can ignite if safety is compromised. Preventing thermal runaway is no longer just about product reliability—it’s about preventing disaster.
UL94 V-0 Fire-Retardant Materials: Definition and Certification
The UL94 V-0 rating is a globally recognized standard for fire safety, certifying that materials self-extinguish within 10 seconds and do not drip burning particles. This ensures they don’t contribute to the spread of fire in the event thermal runaway begins. These certifications help engineers select only the safest materials for battery housings and device enclosures.
How Fire-Retardant Materials Work
Fire-retardant (UL94 V-0) materials use chemical additives that interrupt combustion. When exposed to high heat, they release flame-inhibiting vapors, form char layers that insulate surfaces, and slow heat transfer. This multi-barrier system buys valuable time for shutdown protocols to activate and limits damage to immediate surroundings.
Key Applications of UL94 V-0 Certified Materials
Industries rely on UL94 V-0 materials in:
- Electric vehicle battery packs
- Consumer electronics: smartphones, laptops, tablets
- Industrial robotics and automation systems
- Medical devices and life-support equipment
- Renewable energy storage (solar and wind cell batteries)
For a deeper look at how these adhesives integrate in EV battery packs, see our selection guide for thermal conductive adhesives.
Types of Fire-Retardant Materials in Battery Systems
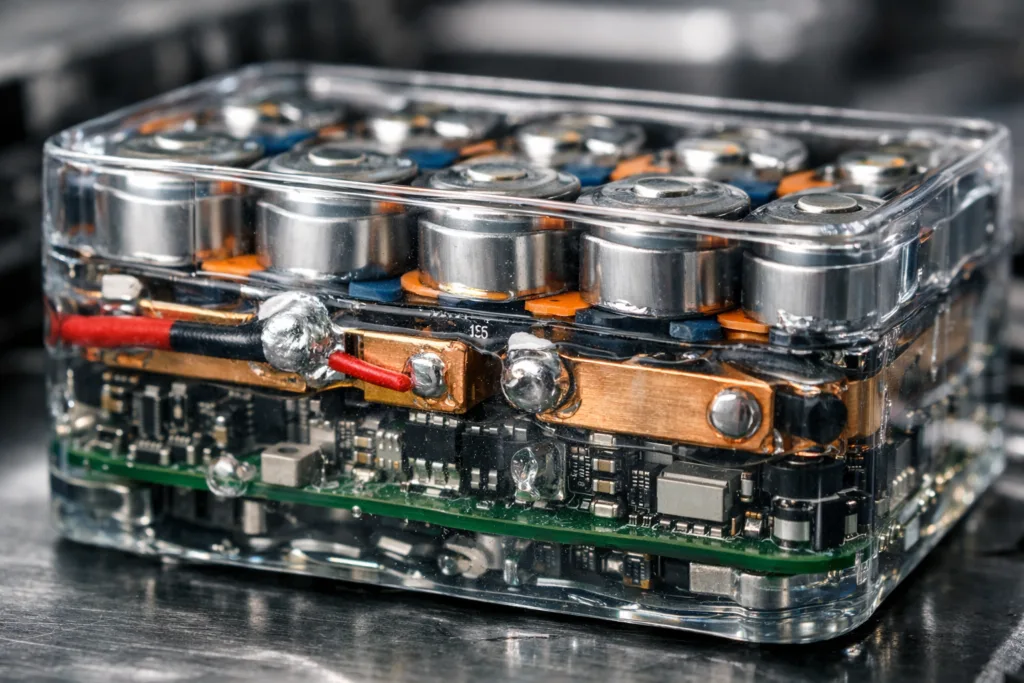
Common UL94 V-0 materials include specialized plastics (like polycarbonate and ABS blends), epoxy potting compounds, and polyurethane structural adhesives. These are engineered to resist ignition and to contain damaged cells, keeping problems localized.
Case Study: Preventing Thermal Runaway in EVs
Over the past three years, automotive manufacturers have dramatically reduced battery fire incidents by switching to UL94 V-0 housing and high-performance adhesives. ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, observed that batteries potted with epoxy compounds (rated V-0) maintained their structure even when single cells failed, limiting the spread of heat and combustion.
Fire-Retardant Adhesives for Electronics Assembly
Adhesives like epoxy and polyurethane are often used in electronics assembly for battery modules, circuit boards, and internal shields. These not only bond components but also add flame resistance at every connection point. Learn more about epoxy adhesive solutions for flame-retardant applications.
Design Guidelines for UL94 V-0 Compliance
Certified fire-retardant materials must achieve strict test results: self-extinguishing, minimal smoke, and zero drip. Engineers should:
- Use all V-0-rated materials at junctions and housings
- Validate designs via simulated thermal runaway tests
- Apply potting or encapsulation to isolate hot spots
- Document and trace material sources for every batch
Testing Protocols for Fire-Retardant Solutions
Standard testing includes vertical burn tests, flame spread assessments, and exposure to overcharge cycles. Only products passing UL94 V-0 can be specified for critical electronics. For example, industrial adhesives undergo repeated high-temperature cycles before release.
Comparing UL94 V-0 vs. Lower-Rated Materials
| Property | UL94 V-0 | UL94 HB/FA |
|---|---|---|
| Extinguishes within | 10 seconds | Not specified |
| Dripping | None | May drip flaming particles |
| Smoke Generation | Minimal | Moderate to High |
| Battery Safety | High | Low–Moderate |
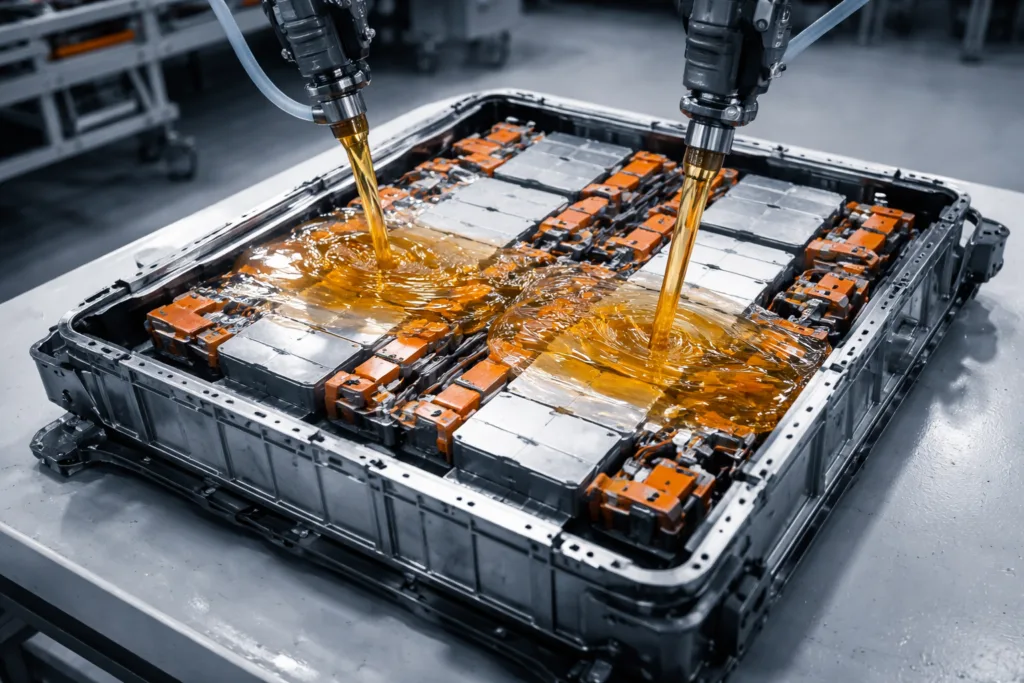
Integrating UL94 V-0 Solutions in Manufacturing
To meet modern safety standards, manufacturers use automated systems to apply V-0 adhesives and potting compounds precisely. This ensures even coverage and predictable fire-retardant performance.
Material Selection Criteria for Battery Enclosures
Selection should balance fire rating, mechanical strength, chemical compatibility, and cost. For large production runs, engineered blends of epoxy and polycarbonate often deliver the most reliable results. Read more on industrial adhesives for battery enclosures.
Challenges in Implementing Fire-Retardant Materials
While materials exist, achieving consistent V-0 compliance in high-volume manufacturing demands precise formulation control and strict supplier audits. Manufacturers must also ensure long-term aging and chemical resistance are maintained, especially in harsh environments.
Regulatory Trends and International Standards for Fire Retardancy
Beyond UL94 V-0, global standards like IEC 60695 and EU directives increasingly require lifetime fire safety, not just initial certification. This means higher-quality materials and routine inspection even after assembly.
Common Failures and Troubleshooting in Fire-Retardant Protection
Failures often stem from poor material mixing, incomplete curing, or incompatible surface conditions. Assembly guidelines recommend surface cleaning, use of compatible primers, and regular process validation to minimize risks.
Step-by-Step Guide to Applying UL94 V-0 Adhesives
- Clean and dry all surfaces (especially plastics and metals)
- Select matching UL94 V-0 epoxy or polyurethane adhesives
- Measure and mix according to supplier instructions
- Apply in thin, uniform layers
- Allow adequate fixture and cure time
- Test with simulated thermal stress before final use
Monitoring and Maintenance for Safety Assurance
Routine checks ensure that potting and encapsulation layers remain intact. Replace damaged covers and maintain strict traceability for all fire-retardant components.
The Future of Fire-Retardant (UL94 V-0) Materials in 2026
By 2026, manufacturers expect further improvements in multi-functional fire-retardant materials. Advances in polymers and hybrid adhesives promise better mechanical and flame resistance, without sacrificing performance or cost efficiency.
Preventing Thermal Runaway: Fire-Retardant (UL94 V-0) Solutions
In summary, fire-retardant materials with UL94 V-0 certification play a pivotal role in containing thermal runaway events. Their use across industries, particularly in battery engineering, ensures safer products and lower risk of catastrophic failures. By integrating these materials with proven adhesives and following strict testing and traceability standards, companies can stay ahead in both compliance and protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thermal runaway in batteries?
Thermal runaway is a rapid temperature increase in a battery, triggered by exothermic reactions, that leads to uncontrollable heating, fire, or explosion.
How do UL94 V-0 materials prevent fires?
UL94 V-0 materials self-extinguish flames quickly, preventing the spread of fire and containing heat within the battery or device enclosure.
Where are fire-retardant adhesives used?
They are used in battery modules, circuit boards, electric vehicles, and consumer electronics to bond and insulate sensitive components.
What tests ensure UL94 V-0 certification?
Tests include vertical burn, flame spread, drip resistance, and thermal cycling to validate non-flammability and durability in real conditions.
Can lower-rated materials stop thermal runaway?
No; only UL94 V-0 certified compounds guarantee rapid flame suppression and safe containment of battery failures.
What’s new for fire-retardant technology in 2026?
Innovations include hybrid flame inhibitors, more versatile adhesives, and polymers that better resist aging and harsh conditions in high-demand applications.
Related Reading
- Battery Potting Compounds: Silicone vs. Polyurethane—Pros & Cons in Modules
- Unlocking Epoxy Performance: The Impact of Glass Transition Temperature in Industrial Use
- Structural vs. Thermal Adhesives: 7 Differences for CTP Battery Design
- Mixing Ratios & Curing Profiles: Achieving Industrial-Grade Epoxy Bonds
- Top Factors When Selecting Thermal Conductive Adhesives for EV Battery Packs