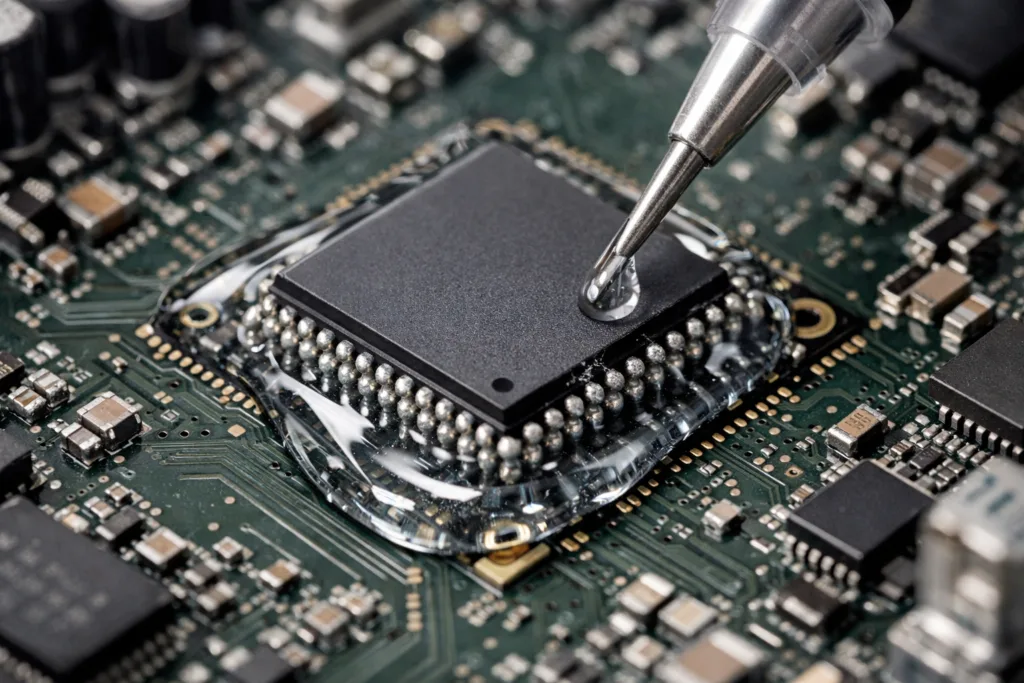
Understanding Industrial Epoxy Adhesive
Industrial epoxy adhesive is a high-performance bonding material used to join metals, composite parts, ceramics, glass, and even engineered plastics. Epoxy adhesive blends resin and hardener to form strong chemical links as it cures—building reliable joints in manufacturing, assembly, construction, and repair. These adhesives are prized for their strength, durability, and resistance to heat and chemicals, making them the first choice for demanding applications like automotive bodywork, aerospace parts, electronics assembly, and industrial maintenance.
Strength and Mechanical Performance
Epoxy adhesives offer outstanding mechanical strength. Industrial grades achieve lap shear strengths over 30 MPa and tensile strengths above 40 MPa, based on test standards like ASTM D1002. These numbers mean structural bonds can withstand considerable force before failing. Unlike mechanical fasteners, a well-prepared epoxy joint shares stress across the bonded surface, reducing weak points and resisting vibration, movement, and cycling loads. For metal bonding, epoxy adhesives rival welding in many applications—without thermal distortion or oxidation risks.
Key Factors Affecting Bond Strength
- Adhesive chemistry: Two-part (2K) systems with tailored resin/hardener ratios provide greater strength and performance options than single-part (1K) products.
- Substrate preparation: Degreasing, abrasion, or grit blasting boosts bondability, especially for metals. Epoxy bonds best to clean, rough surfaces.
- Mixing & application: Precise mix ratios, thorough blending, and steady bead application ensure uniform cure.
- Fixturing: Clamping keeps parts aligned and maximizes adhesive contact during curing.
Strength in Metal and Composite Bonding
Epoxy adhesive for metal stands out because it forms deep chemical links with steel, aluminum, copper, and alloys. This bond can surpass the metal’s own yield strength in shear and peel scenarios. Composite parts—like carbon fiber or fiberglass—also use epoxy for their core lamination, joint assembly, and edge reinforcement. Epoxy’s low shrinkage and minimal stress on substrates preserve dimensional accuracy throughout the curing process.
Resistance to Temperature and Chemicals
Industrial epoxy adhesives resist high heat and harsh chemicals far better than many other glues. Once cured, typical grades withstand continuous temperatures from –40°C up to 120°C, with specialized formulations extending up to 200°C or more. Thermal cycling tests reveal that epoxy remains stable after hundreds of hot/cold cycles, making it ideal for engine assemblies and exterior construction panels. Chemical resistance depends on the chosen formula but generally includes defense against oils, fuels, solvents, weak acids, and water. For maximum protection, ZDS offers epoxy systems tested per REACH, RoHS, and VOC standards for environmental and user safety.
Comparison Table: Epoxy vs. Other Industrial Adhesives
| Adhesive Type | Chemistry | Substrates | Typical Strength (MPa) | Temperature Resistance (°C) | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 2K Resin/Hardener | Metals, Composites, Ceramics, Glass | 30–40+ (shear) | -40 to 200+ | Structural bonding, metal joinery, composite repairs |
| Polyurethane | 1K/2K | Plastics, Foam, Metals | 15–25 | -30 to 120 | Flexible seals, vibration damping |
| Acrylic | 2K | Plastics, Metals | 12–28 | -40 to 120 | Quick repair, fast cure |
| Silicone | RT/Heat Cure | Glass, Metals, Plastics | 5–10 | -50 to 250 | Elastomeric gasketing, flexible bonding |
| Cyanoacrylate | Instant Cure | Plastics, Metal, Rubber | 10–25 | -20 to 80 | Small parts, quick assembly |
Industrial Epoxy Adhesive: Core Properties Explained
Let’s look deeper at what gives industrial epoxy adhesives their workhorse reputation in factories and assembly lines:
- Cure and Pot Life: Cure time depends on the type. Fast-setting epoxies may reach handling strength in minutes. Extended-pot-life grades—more than 90 minutes—allow large assemblies or intricate positioning. Most 2K epoxies cure fully in 8–24 hours at room temperature, though heat, humidity, and formulation can change speed.
- Hardness and Modulus: Epoxy adhesives cure to a hard, thermoset state. Typical Shore D readings range from 75 to 90, creating a tough, inflexible bond ideal for rigid assemblies.
- Viscosity: Varies by formula—thin epoxies (200–1,000 cP) flow easily into joints, while pasty epoxies (10,000–100,000 cP) help gap filling or vertical applications.
- Elongation: Most industrial grades stretch 1–10% before failure, which is enough for parts that need minor flex but not rubber-like movement.
- Thermal and Chemical Resistance: By blending tough resins with special additives, ZDS epoxy adhesives are tailored for use in offices, outdoors, engine bays, or chemical plants.
Epoxy Adhesive for Metal Bonding
Want to bond metal parts for assemblies or repairs? Epoxy adhesive for metal delivers unmatched strength, gap-filling capability, and lasting protection against corrosion. Unlike spot welding, an epoxy bond covers the entire joint, distributing loads evenly and avoiding heat distortion. Typical applications include automotive body panel assembly, bus and rail car builds, electrical enclosures, and even appliance manufacturing. Surface prep is vital: degrease well, abrade for texture, and consider primers for aluminum and engineered alloys to improve adhesion.
Factory-Tested Performance Metrics
- Lap shear strength (ASTM D1002): Over 30 MPa on steel, aluminum, and copper
- T-peel strength (ASTM D1876): 10–15 kN/m for advanced metal prep
- Salt spray resistance (ASTM B117): No failure after 500 hours in aggressive corrosion environments
- Thermal cycling: Stable after 1,000 cycles from –40°C to 120°C
In demanding projects, ZDS customizes epoxy adhesives with tailored open times, viscosities, and cure profiles for automated dispensing, slot-die spreading, or roll-coat application.
Epoxy Adhesive for Composite Bonding
Composites like carbon fiber, fiberglass, and honeycomb structures depend on epoxy adhesives for both manufacture and repair. The resin’s chemistry matches the matrix of most composite materials, guaranteeing compatibility and superb mechanical performance. Epoxy maintains composite integrity against heat, chemicals, and vibration. For aerospace, sports equipment, and high-end automotive, ZDS provides 2K and film/tape-format epoxies for laminating, skin-to-core bonding, and repairs.
Process Tips and Substrate Preparation
- Degrease all surfaces with solvent.
- Abrade with sandpaper or media blast, then clean again.
- Apply mixed epoxy with a notched trowel, bead dispenser, roll-coater, or spray as needed.
- Fixturing and clamping ensure contact and prevent shift during cure.
- Allow adequate cure time based on part thickness and formula. Post-cure heat increases strength.
Other Industrial Substrates: Ceramics, Glass, Plastics, and Stone
Industrial epoxy adhesives also bond ceramics, glass, engineered plastics such as ABS (Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene), PC (Polycarbonate), PA (Polyamide), and even stone or tile. Proper substrate preparation is critical: corona or plasma treatment helps low-energy plastics, while abrasion works best for ceramics and glass. For stone and flooring, high-viscosity epoxies fill gaps and create robust, moisture-resistant seals. ZDS supplies formulas that comply with ISO 9001 quality standards and are shipped with SDS safety documentation.
Dispensing and Automation Solutions
- Static mixers for 2K cartridges—consistent mix and easy application
- Bead, slot-die, and roll-coat machinery—for bulk bonding and assembly
- Automated robots—precision dispensing for electronics, automotive, and appliance lines
Quality Control and Compliance
Every batch of industrial epoxy adhesive undergoes rigorous quality control. ZDS tests samples for lap shear, peel, tensile, and exotherm (heat released during cure). Salt spray and thermal cycle testing ensure long-term durability. For compliance, products meet or exceed REACH, RoHS, and VOC regulations. Lot traceability means every cartridge or pail is logged from raw materials to final shipment. Proper storage (5–30°C, dry, closed containers) preserves shelf life and performance.
Documentation and Traceability
- Batch test reports—mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties
- SDS (Safety Data Sheets)
- ISO 9001 certificates
- REACH/RoHS compliance statements
Expert insight: “The right industrial epoxy adhesive transforms assembly speed and durability. But prepping parts and matching chemistry to use is what delivers lasting strength and reliability.”
Industrial Epoxy Adhesive: Key Applications & Best Practices
Industrial epoxy adhesives are used across sectors:
- Automotive: Bonding body panels, crash beams, bumper cores, battery casings
- Aerospace: Composite skin lamination, metal-to-composite joints, repair patches
- Electronics: PCB assembly, sensor encapsulation, heat-resistant housings
- Construction: Structural glazing, stone/ceramic bonding, metal facade installation
- Stone/Flooring: Tile fixing, substrate repair, moisture-resistant sealing
For best results, always follow manufacturer mixing instructions, use recommended surface prep, and allow full cure before loading assemblies. In projects that demand reliability, ZDS engineers provide technical guidance and rapid sample turnaround for trial and validation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes industrial epoxy adhesive stronger than other adhesives?
Epoxy adhesive uses two reactive components that form very strong, cross-linked chemical bonds. This provides high shear, peel, and tensile strength, especially for metals and composites.
Can epoxy adhesive be used for metal repair and fabrication?
Yes. Industrial epoxy adhesive bonds steel, aluminum, and copper in repairs, body assembly, and metal structure fabrication, replacing welding or mechanical fastening in many cases.
What is the temperature limit for cured epoxy adhesive?
Most industrial epoxy adhesives work from –40°C to 120°C; specialty types resist up to 200°C or more, suitable for engine bays or exterior panels.
Which surface preparation steps improve epoxy bonding?
Degreasing, abrasion, and sometimes primers are vital. Clean, rough, and dry surfaces guarantee maximum bond strength and durability.
Is industrial epoxy adhesive resistant to chemicals and moisture?
Yes. Epoxy adhesive resists oils, fuels, solvents, water, and weak acids. Performance varies by grade, so select an epoxy tailored for your environment.
Where can I source high-performance industrial epoxy adhesive?
Suppliers like ZDS offer a full line of industrial epoxy adhesives for metal, composite, glass, and plastics, with technical support and custom formulations.