Understanding the Role of Thermal Management in EV Battery Packs
Effective thermal management is the cornerstone of safe, long-lasting, and high-performing EV battery packs. With electric vehicles powering our roads in 2026, battery temperatures can reach critical levels during operation and charging. If not properly managed, overheating triggers performance drops and decreases battery lifetime, sometimes even posing safety hazards. Engineers now prioritize advanced cooling strategies—and thermal conductive adhesives are front and center.
What Are Thermal Conductive Adhesives?
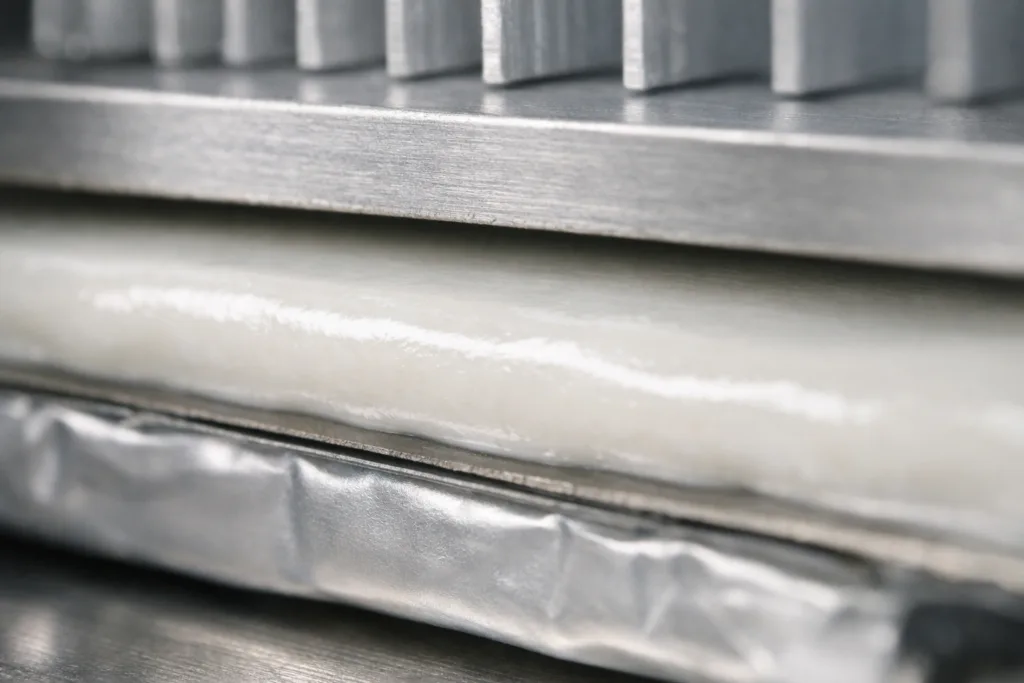
Thermal conductive adhesives are specialized bonding materials formulated to transfer heat efficiently between cell components and cooling mechanisms. Unlike standard adhesives, they combine structural bonding with high thermal conductivity, so heat dissipates from sensitive cells to heat sinks or cooling plates. This dual-functionality supports both fastening and temperature control inside EV packs.
Why Use Thermal Conductive Adhesives in EV Battery Packs?
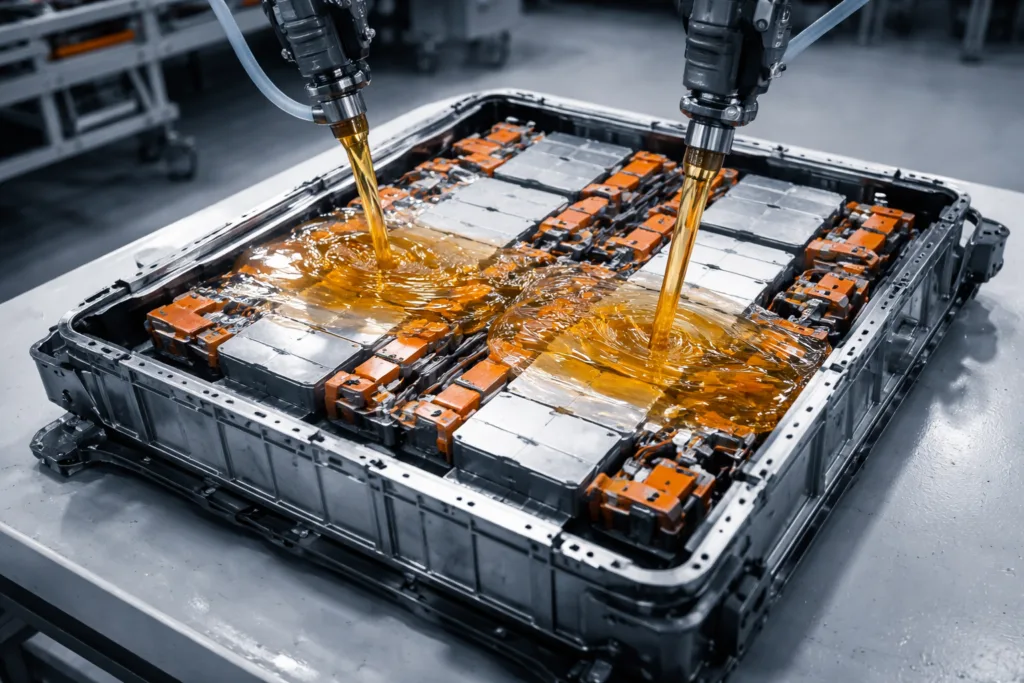
The use of these adhesives has surged as EV designs become denser and power demands increase. Without robust heat dissipation, hotspots form between battery cells—undermining reliability. By providing low thermal resistance and strong adhesion, thermal conductive adhesives help balance temperature, minimize cell degradation, and prevent thermal runaway events.
- Faster heat transfer reduces risk of overheating
- Improved mechanical stability during vibration and shock
- Enhanced cycle life for high-power battery assemblies
Types of Thermal Conductive Adhesives for EV Batteries
Adhesive chemistries vary to suit different manufacturing requirements. Common types include:
- Epoxy adhesives: Offer high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength; ideal for rigid cell-to-metal bonding (epoxy adhesive product details).
- Silicone-based adhesives: Flexible, vibration-resistant, and generally suited for dynamic joints.
- Polyurethane adhesives: Provide shock absorption and moderate thermal dissipation (polyurethane structural adhesive breakdown).
- Acrylic adhesives: Fast-curing, suitable for automated assembly lines needing rapid throughput.
Thermal Conductivity Ratings Explained
Thermal conductive adhesives are measured in watts per meter-Kelvin (W/m·K). The higher the rating, the faster heat moves across the bond line. For EV battery packs, values typically range from 0.6 to 4 W/m·K. Tailoring the rating is critical—too low, and heat lingers at the interface; too high may compromise flexibility. Most engineers target a balance that aligns with the battery’s cooling strategy.
| Adhesive Type | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 1.0 – 3.5 | Cell-to-heat sink, rigid chassis mounting |
| Silicone | 0.8 – 2.5 | Flexible connections, vibration-prone joints |
| Polyurethane | 0.6 – 2.0 | Shock-absorbing, large-area bonding |
| Acrylic | 0.7 – 2.8 | Fast-paced automated lines |
How Curing Profiles Affect Performance
Curing profile describes how an adhesive transforms from liquid/paste to solid—usually through heat, moisture, or UV exposure. Selection influences throughput, bond strength, and thermal pathway quality. For EV batteries, heat-curing epoxies deliver dense, rigid bonds, while moisture-curing silicones accommodate expansion and contraction. UV-curable formulas also exist for speed but may limit use in less accessible areas.
Application Techniques for Optimal Thermal Management
Applying thermal conductive adhesives correctly is just as important as the product itself. Key steps include:
- Surface Preparation: Clean, degrease, and optimize surface energy—see surface preparation guide for best practices.
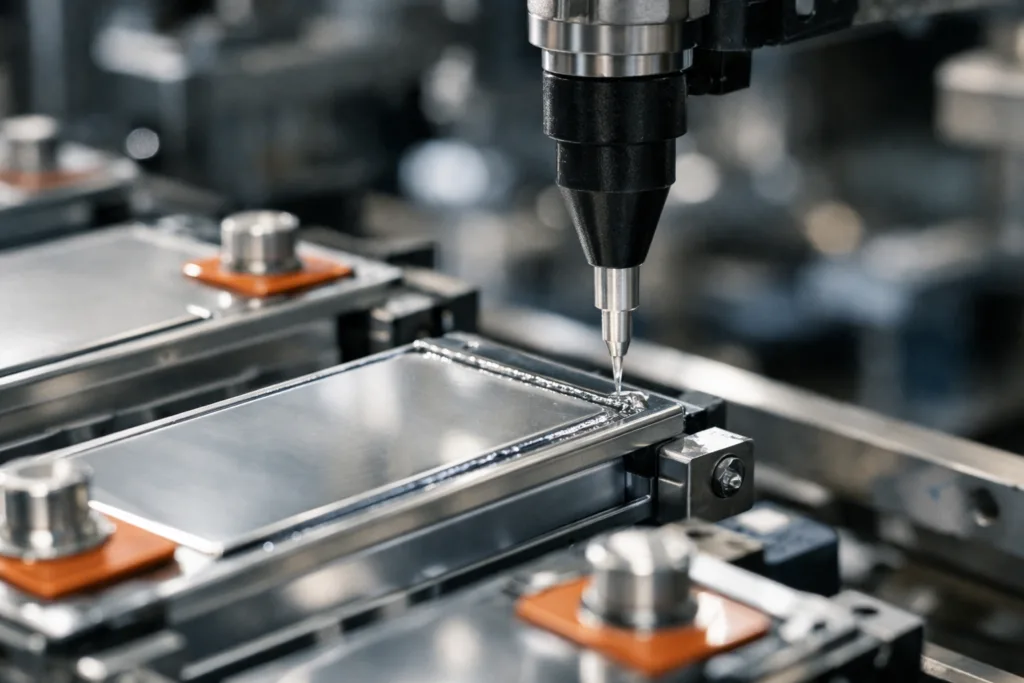
- Precise Dispensing: Use robotic dispensers for uniform thickness across cell interfaces.
- Controlled Cure: Follow time-temperature curves to avoid voids or incomplete bonding.
- Post-assembly Inspection: Thermal imaging can verify even heat distribution.
Typical Challenges When Using Thermal Conductive Adhesives
Despite their advantages, EV engineers face several hurdles:
- Maintaining thin, void-free adhesive lines across large cell arrays
- Balancing bond strength with reworkability—many strong adhesives are semi-permanent
- Ensuring process repeatability in high-volume manufacturing scenarios
- Compatibility with diverse substrate materials (aluminum, nickel, composite housings)
Safety and Compliance: Why It Matters
Stringent safety standards govern EV batteries globally. Thermal conductive adhesives help maintain pack temperatures within regulatory limits. Reliable performance under thermal cycling and humidity aging is essential—these properties protect against catastrophic failures. Always confirm adhesive solutions meet automotive standards (UL, ISO, IEC) relevant in your region.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Thermal Conductive Adhesive
Choosing the ideal adhesive involves more than just thermal ratings. Critical factors include:
- Substrate compatibility (metal, plastic, composite)
- Required cure speed and open time
- Mechanical flexibility
- Long-term aging resistance: thermal cycling, chemicals, humidity
- Regulatory certifications and regional compliance
Recent Advancements in Adhesive Technology for Electric Vehicles
Adhesive R&D continues to push the limits for thermal management:
- Nanoparticle-enhanced formulas: Leverage graphene or boron nitride for higher conductivity with lower density
- Low-viscosity liquids: Flow easily into micro gaps for void-free bonds
- Hybrid chemistries: Blend silicone and epoxy for balance of flexibility and strength
- Smart self-healing materials: Automatically repair minor bond damage over time
Application Examples: Real-World Use Cases
In practice, EV manufacturers use thermal conductive adhesives for several key assemblies:
- Bonding cylindrical or pouch cells to cold plates
- Attaching sensors or electronic modules for direct heat transfer
- Sealing busbars and terminals against thermal cycling
- Encapsulating PCBs that monitor battery health
How ZDS Adhesive Approaches EV Battery Pack Challenges
From an assembly-line viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, thermal management starts with comprehensive substrate testing. Selection depends on bond-line thickness, ambient humidity, and target conductivity—with lap shear and peel tests performed on representative nickel and aluminum samples. Engineers monitor cycle life under 60°C ramp cycles and evaluate chemical exposure against typical battery electrolytes. Using these numbers, they guide manufacturers toward adhesives with a proven record of mechanical and thermal reliability in both prototyping and mass production.
Thermal Conductive Adhesives for EV Battery Packs: A Selection Guide
When selecting thermal conductive adhesives for EV battery packs, always blend data with hands-on experience. Review thermal conductivity specs, but also demand real-world testing under operational conditions. Account for all elements: surface prep, dispensing, cure profile, post-assembly tolerance, and aging resistance. Consider collaborative trials with adhesive specialists to validate process stability at scale. Ultimately, a great adhesive decision extends battery life, boosts reliability, and keeps assembly costs predictable.
Conclusion
Thermal conductive adhesives are a crucial tool for managing heat in modern EV battery packs. By choosing the right chemistry and optimizing application, manufacturers protect batteries, enable rapid charging, and extend pack lifespan. With new advances in formulation, the choices in 2026 are more robust and specialized than ever—making careful selection essential as electric vehicles continue to evolve.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of thermal conductive adhesives in EV batteries?
They efficiently transfer heat from battery cells to cooling systems, preventing overheating and promoting safety in electric vehicles.
How is thermal conductivity measured in adhesives?
It’s measured in watts per meter-Kelvin (W/m·K), indicating how efficiently heat moves through the bonded interface.
Which adhesive type offers the highest thermal conductivity for battery packs?
Epoxy adhesives generally provide the highest ratings and strongest bonds for rigid, high-performance assemblies.
Why is surface preparation important before applying thermal adhesives?
Proper cleaning improves bond strength, reduces risk of adhesion failure, and ensures efficient thermal transfer across interfaces.
Are thermal conductive adhesives affected by vibration and shock?
Silicone and polyurethane types are more flexible, making them better choices for areas subject to high movement or impact.
Can adhesives help meet EV battery safety standards?
Yes. By maintaining stable temperatures, thermal conductive adhesives help manufacturers comply with strict safety and reliability regulations.
Related Reading
- Epoxy vs Silicone vs Polyurethane: Choosing Your Best Fit
- Industrial Adhesives: Essential Types, Uses & a Selection Roadmap
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Picking the Perfect Industrial Adhesive
- Rising Above the Heat: Advancements in High-Temperature Adhesives
- Smart Adhesive Choices for Solar, EV & Wind Energy