Introduction: Why Fast Charging Demands Superior Thermal Shock Resistance
As fast charging cycles become the new normal for electric vehicles and battery-powered devices, the role of adhesives in thermal shock resistance has never been more critical. Thermal shock resistance: testing adhesives for fast charging cycles is at the forefront of designing batteries that last longer and perform reliably. Rapid charging generates significant heat and exposes materials to repeated temperature swings. These stresses can degrade conventional adhesives, leading to cracked bonds, failures, and safety risks. Choosing and testing the right adhesive is not just science—it’s essential for manufacturers, engineers, and anyone seeking stable performance in next-generation battery systems.
Understanding Thermal Shock: The Basics
Thermal shock occurs when a material is rapidly exposed to extreme temperature changes. In battery applications, fast charging cycles cause internal temperatures to spike quickly and then cool down, placing both the cell and adhesives under tremendous stress. This phenomenon can result in expansion or contraction, micro-cracking, and bond line separation, especially if the adhesive’s properties don’t match those of the joined substrates. The result? Electrical, mechanical, and thermal failures that threaten device safety.
The Role of Adhesives in Battery Integrity
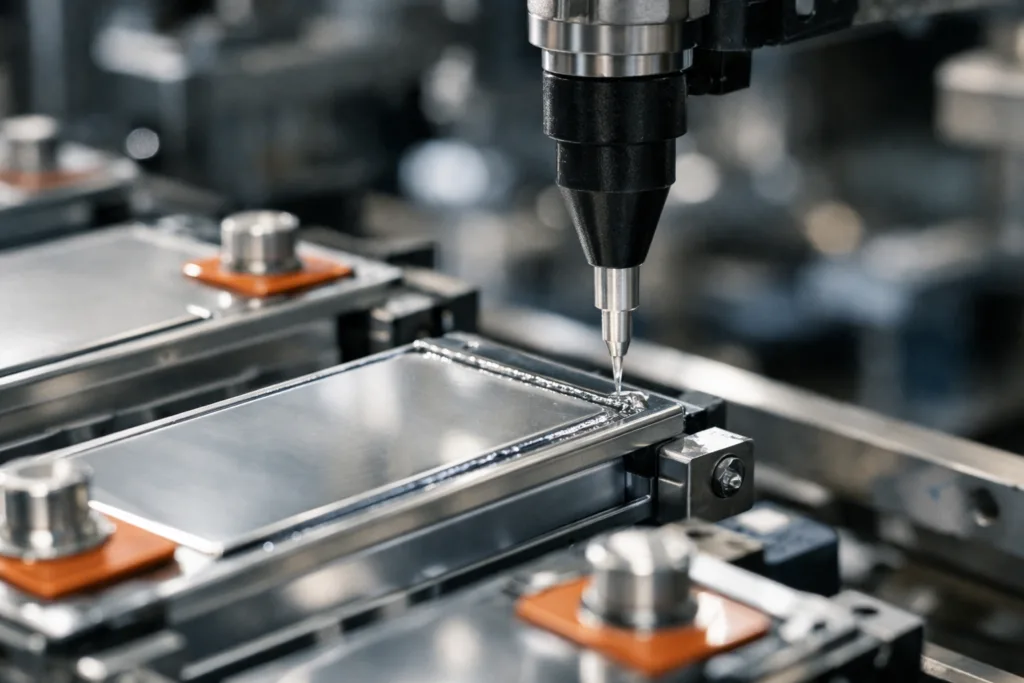
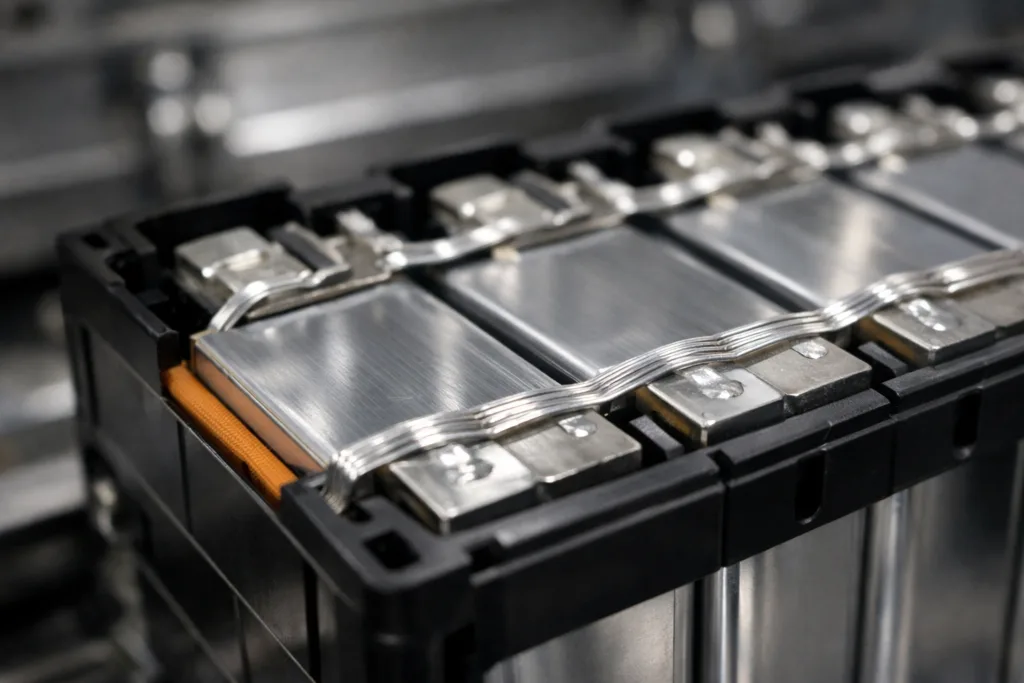
Within modern energy storage, adhesives fulfill more than just bonding. They enable thermal management, prevent moisture invasion, reduce vibration, and block pathways for potential short circuits. In fast charging, adhesives face quick shifts from 20°C to 60°C or higher. Failure to withstand these swings undermines not just the battery but the entire assembly. That’s why selecting an adhesive with proven thermal shock resistance is a central engineering decision.
Challenges in Fast Charging: Adhesive Performance Requirements
Fast charging introduces several interconnected challenges. Rapid temperature cycling increases stress on the adhesive bond, while high power density raises thermal gradients throughout the battery pack. Adhesives must absorb these stresses:
- Wide temperature range tolerance
- Excellent thermal conductivity without sacrifice to mechanical strength
- Long-lasting elasticity to resist fatigue
- Chemical and humidity resistance
- Compatibility with metals, ceramics, and plastics
For those assembling batteries or designing modules, the right adhesive maintains structural integrity, allowing active materials to operate as intended even after hundreds or thousands of charging cycles. See how industrial adhesive technology addresses similar needs in industrial adhesives.
Testing Methodologies for Thermal Shock Resistance in Adhesives
How do engineers test adhesives for thermal shock? Standard methods include:
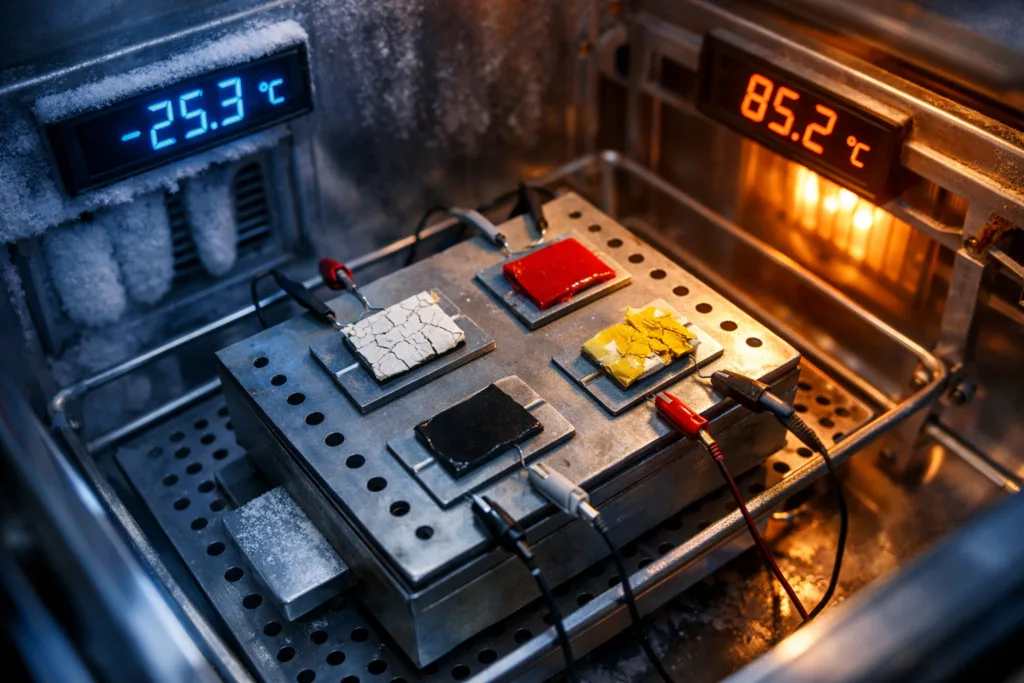
- Cyclic thermal shock testing: Repeatedly expose samples to hot (up to 100°C+) and cold (down to -40°C) environments
- Pulsed heating: Mimic real fast-charging cycles to observe bond behavior
- Lap shear, peel, and tensile strength measurements before and after thermal cycling
- Optical inspection for cracks, delamination, or color change (yellowing, clouding)
- Electrical continuity testing to ensure insulation integrity
Factories might perform elaborate accelerated testing using environmental chambers and multi-axis stress rigs. Results determine if an adhesive will survive not just initial rapid charging, but years of real-world usage.
Key Adhesive Properties for Thermal Shock Resistance
Adhesives engineered for thermal shock resistance exhibit several defining traits:
- Optimized glass transition temperature (Tg)
- Controlled modulus and flexibility for stress relief
- Stable chemical composition even after repeated heat/cool cycles
- Low water absorption to prevent hydrolytic degradation
- Precise filler content, sometimes leveraging nano-fillers for enhanced thermal performance
Learn more about optimizing these traits in epoxy systems at How Nano-Fillers Revolutionize Epoxy Thermal Conductivity for Metal Products.
Comparing Common Adhesive Types for Fast Charging Cycles
| Adhesive Type | Thermal Shock Resistance | Typical Battery Use | Key Pros | Key Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | High (toughened grades) | Cell bonding, busbar adhesive | Strong, good insulation, chemical resistance | Brittle if not customized; slow cure |
| Silicone | Excellent | Potting, gaskets, vibration damping | Elastic, wide temperature range | Lower mechanical strength; costly |
| Polyurethane | Good (low-modulus types) | Encapsulation, cell sealing | Flexible, moisture resistant | Sensitivity to water, sometimes slow cure |
| Acrylic | Moderate | Structural bonds | Fast set, bonds most surfaces | UV resistance varies |
Principles Behind Adhesive Thermal Shock Resistance
Thermal shock resistance in adhesives hinges on several scientific principles:
- Cohesive strength: The internal strength resists cracking within the adhesive
- Adhesion: The bond to substrates must accommodate movement and stress
- Elasticity: The ability to flex without losing shape or grip
- Thermal conductivity: Vital for spreading heat uniformly
The interplay of these factors ensures that the adhesive neither loses bond nor becomes a failure point when the battery cycles rapidly from cool to hot and back.
Case Study: Adhesive Testing for EV Fast Charging
Consider a battery module facing charging rates that double internal temperature within 10 minutes. Engineers select several adhesives, apply them to metal-cell interfaces, and subject them to 1000 cycles ranging from 25°C to 80°C, with rapid transitions. Important test parameters include:
- Lap shear and peel strength before and after cycling
- Visual inspection for color change, cracks, and delamination
- Thermal imaging of the bond line
- Dielectric strength retention
The adhesives that pass must provide not just mechanical hold, but also sustain insulation and prevent moisture ingress throughout thousands of cycles. For readers interested in further reliability technology, check out 10 Essential Factors for Reliable Adhesives in EV Battery Liquid Cooling Plates.
Experimental Results in the Field
Real-world testing has shown that toughened epoxy adhesives, advanced silicones, and well-formulated polyurethanes generally withstand rapid temperature change the best. However, even the highest-rated adhesives must be custom-matched to each substrate and operating environment. A cure mismatch or improper thickness can create hotspots, accelerating molecular breakdown and leading to premature bond failures.
Importance of Adhesive Selection for Battery Applications
The choice of adhesive isn’t just about holding parts together—it’s about protecting battery performance and user safety. Key considerations include:
- Will the adhesive keep the module sealed through all operating temperatures?
- How well does it manage heat and prevent short circuits?
- Can it isolate electrical pathways safely?
- Does it offer long-term chemical resistance?
These questions drive innovation in formulations and in battery system design.
Common Failure Modes During Fast Charging Cycles
After repeated fast charging, adhesives may fail in several ways:
- Cracking due to thermal expansion mismatch
- Color changes (yellowing) caused by heat cycles
- Surface delamination under cyclic stress
- Loss of electrical insulation
- Accelerated aging and water absorption
Preventing these failures begins with rigorous in-lab testing, which sets screening standards for production lines.
Design Decisions for Maximizing Thermal Shock Resistance
From an assembly-line viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, material selection is a step-by-step process. Application engineers start by understanding the expected temperature range, dwell times, substrate materials, and desired bond-line thickness. Standard decision rules include:
- Using primers or plasma treatment on low-energy surfaces like PP/PE
- Specifying pot life and open time according to fixture times
- Testing both lap shear and peel strength after thermal cycling
- Ensuring the adhesive is stable under humidity and chemical exposure
This hands-on approach is rooted in preventing predictable failure modes and improving reliability in battery assemblies.
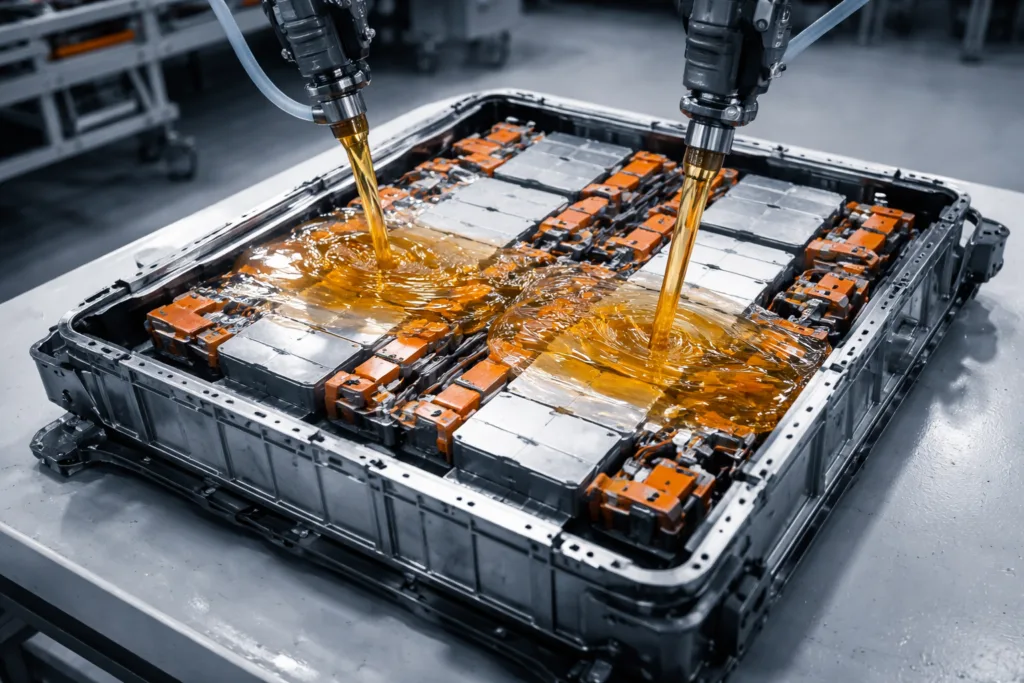
Advanced Solutions: Nano-Fillers, Hybrid Formulations, and Smart Potting
Recent breakthroughs show that integrating nano-fillers can significantly improve thermal conductivity and shock resistance in epoxies. Hybrid adhesives blend silicone elasticity with epoxy strength, and smart potting solutions combine layered materials that buffer temperature swings. For specialized battery applications—including liquid cooling plates and flexible pouch cells—these advanced materials are uniquely effective.
Adhesive Processing and Application Best Practices
Maximizing thermal shock resistance involves strict process controls:
- Surface preparation using plasma or chemical primers
- Precise mixing and uniform application
- Controlled cure profiles (temperature and humidity management)
- Quality assurance testing for every production batch
Production lines adopt these best practices to prevent variables that can undermine adhesive performance over time.
Trends in Testing Methodology: Accelerated and Digital Techniques
Major manufacturers now use digital thermal imagers, real-time bond monitoring, and accelerated cycling rigs to test adhesives in simulated fast charging environments. Automated reporting and AI-based analysis spot weak points before they reach mass production.
Thermal Shock Resistance: Testing Adhesives for Fast Charging Cycles
It is clear that thermal shock resistance: testing adhesives for fast charging cycles ties together advanced material science and practical assembly-line wisdom. As battery technologies push the limits of speed and longevity, rigorous testing—paired with smart design—ensures adhesives are up to the challenge. Whether you’re a process engineer, quality manager, or product developer, understanding these details is essential for building trustworthy power storage solutions in 2026 and beyond.
Conclusion: Future-Proofing Battery Assemblies with Smart Adhesive Choices
Thermal shock resistance will remain a decisive factor as charging systems evolve. Engineers and manufacturers who invest time in adhesive testing and selection will protect battery safety, boost durability, and support devices that withstand the toughest demands. By prioritizing properties like elasticity, compatibility, and chemical resistance, and by adopting advanced testing protocols, the battery industry can advance into the future—faster, safer, and smarter.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is thermal shock resistance in adhesives?
Thermal shock resistance in adhesives means their ability to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or losing bond strength, which is vital for batteries facing fast charging cycles.
Why are adhesives important for fast charging batteries?
Adhesives help manage heat, maintain mechanical and electrical integrity, and protect against moisture and vibration, especially during the stress of rapid temperature swings in fast charging.
How are adhesives tested for thermal shock resistance?
Engineers use thermal cycling, lap shear and peel tests, visual inspections, and electrical continuity checks to simulate real-world charging conditions and evaluate adhesive performance.
Which adhesive types are best for thermal shock resistance?
Toughened epoxies, silicones, and optimized polyurethanes generally offer the strongest resistance to thermal shock in battery and electronics applications.
What common failures occur with adhesives during fast charging?
Failing adhesives may crack, delaminate, yellow, or lose insulation after repeated temperature changes, threatening both battery performance and user safety.
How can manufacturers improve thermal shock resistance in adhesives?
They can use advanced formulations, prime surfaces, optimize cure profiles, and rigorously test adhesives in simulated conditions to ensure long-term reliability.
Related Reading
- Mastering B-Stage Epoxy: Applications & Storage Strategies for Modern Manufacturing
- Why Dielectric Strength Defines Battery Potting Durability: Essential Insights
- Eliminating Water Absorption in Epoxy Insulation: 2026’s Prevention Guide
- How Toughened Epoxies Boost Metal Bonding Strength in 2026
- Unlocking Epoxy Durability: Discover 13 Key Insights into Glass Transition Temperature