Understanding the Best UV Adhesive for Glass Bonding
Choosing the best UV adhesive for glass bonding isn’t as simple as picking the strongest glue off the shelf. In demanding industrial uses, “best” means a careful balance of high bond strength, long-term clarity, and resistance to environmental aging. Add in requirements for various glass types—like tempered, laminated, or coated glass—and the decision becomes technical and vital. Selecting the right adhesive impacts not only initial assembly quality but also durability under stress, temperature swings, sunlight, and chemicals.
Industrial Requirements for UV Glass Adhesive
Industrial glass bonding goes beyond mere aesthetics. The chosen adhesive must deliver structural reliability and maintain invisible seams for years. Key properties include lap shear strength (measured per ASTM D1002), tensile strength (often >10 MPa), optical clarity (<1% haze), and resistance to yellowing from UV exposure. Durability gets tested through thermal cycling, salt spray (ASTM B117), and humidity aging. ZDS, a leader in adhesive technology, addresses these needs with advanced formulations tailored for manufacturing quality and longevity.
What Makes an Adhesive “Best”?
- Ultimate Bond Strength: Critical for load-bearing or vibration-prone assemblies. Industrial users demand lap shear strengths exceeding 10–15 MPa and T-peel resistance, especially for laminated glass or glass-to-metal joints.
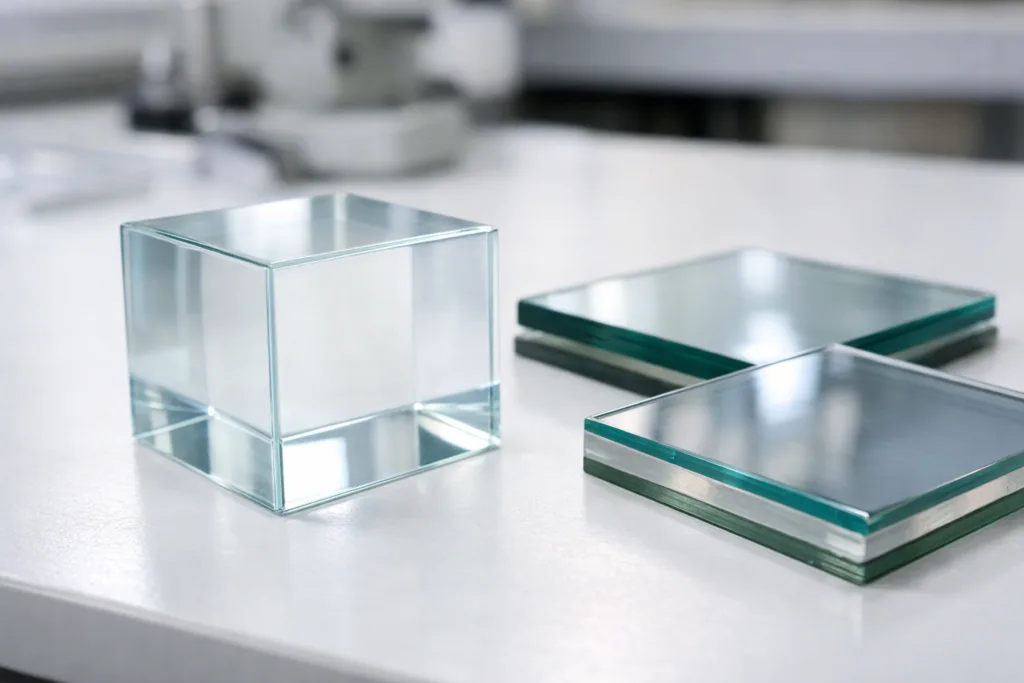
- Crystal-Clear Transparency: Bonds should not cloud, haze, or yellow with time, even under strong UV or heat. The best formulas maintain clarity for years.
- Long-Term Aging Resistance: Adhesives must withstand repeated sunlight, temperature swings, humidity, and chemical cleaning without failing or discoloring.
- Fast, Controlled Cure: UV cure adhesives offer instant handling once exposed to the correct wavelength (typically 365–405 nm UVA), letting production lines move quickly.
- Process Flexibility: From bead dispensing to slot die or reel-to-reel, leading adhesives adapt to various manufacturing setups.
Table: Key UV Adhesive Chemistries for Glass
| Chemistry | Compatible Glass Types | Strength (Lap Shear, MPa) | Transparency | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acrylic (UV Cure) | Clear/Tempered/Laminated | 8–18 | Excellent | Display bonding, architectural glass, furniture |
| Epoxy (UV/dual cure) | Clear/Metal/Coated | 15–22 | Very Good | Glass-to-metal, sensors, high-load parts |
| Silicone (UV/heat cure) | Coated/Low-E/Colored | 3–8 | Good | Flexible joints, sealing, robust outdoor use |
| Hybrid MS Polymer | Tempered/Patterned | 8–12 | Good | Flexible, weatherproof assemblies |
How UV Adhesive Chemistry Affects Performance
The core chemistry of a UV adhesive shapes every aspect of performance. Acrylic-based UV adhesives are industrial favorites for bonding glass due to their fast cure and lasting clarity. These 1K (single-component) resins remain liquid until exposed to a UV lamp, enabling precise placement. Epoxy/UV dual-cures blend ultraviolet and heat activation for deep or shaded bonds, boosting structure and resistance. Silicone UV adhesives add flexibility, working well with glass that expands or contracts in changing temperatures, like windows in building facades.
Transparency and Yellowing
Long-term clarity remains a top requirement. Industrial UV adhesives for glass must resist yellowing under sunlight (UV-A/B). Superior formulas pass accelerated weathering and xenon arc tests, remaining clear after thousands of hours. ZDS, for example, engineers acrylic UV adhesives with UV blockers and stabilizers precisely for such conditions.
Bond Strength in Practice
- Lap Shear: Structural glass bonding for display panels or partitions needs lap shear of 12–20 MPa.
- T-Peel and Impact: Glass doors/windows or electronic enclosures benefit from T-peel strength and shock absorption.
- Edge Quality: Invisible edge bonds are prized in decorative and process glass, so the adhesive’s refractive index should closely match glass.
Types of Glass and Adhesive Matching
Not all glass acts the same. Each type presents unique surface energies, expansion rates, and temperature stabilities. Here’s how to pick the best UV adhesive for glass varieties seen in industry:
Common Glass Types
- Clear Float Glass: Smooth, high-energy surface. Compatible with most UV adhesives with minimal prep.
- Tempered (Toughened) Glass: Higher internal stress. Use UV acrylics or hybrids with some elasticity to handle expansion/contraction.
- Laminated Glass: Contains an interlayer (usually PVB). Bond only to the glass face, as adhesives may not stick well to PVB/plastic unless primed.
- Low-E (Coated) Glass: Reflective metallic coatings can interfere with adhesion. Dual-cure or silicone UV adhesives fare better here.
- Patterned/Textured Glass: Irregular surface; more adhesive spread or controlled rheology needed.
Surface Preparation and Adhesion
Proper surface prep maximizes adhesion. Industrial protocols include degreasing, isopropanol wipes, and sometimes mild abrasion for etched or patterned parts. For plastics or mixed assemblies, use ZDS adhesion promoters or plasma treatment to boost bond strength on low-energy surfaces.
Best UV Adhesive for Glass: Selection Logic
When selecting the best UV adhesive for glass in industrial settings, follow a structured approach. Gather these parameters for your application:
- Glass types involved (clear, tempered, coated, etc.)
- Bond area and load requirements
- Optical needs—crystal clarity, refractive index matching
- Expected aging (UV, chemicals, humidity, temperature)
- Production process (cycle time, dispensing, fixturing)
- Regulatory/environmental constraints (REACH, RoHS, VOC)
Expert tip: Always request lap shear, T-peel, and yellowing resistance data matching your specific substrates and intended use.
Selection Steps
- Identify Substrate: Match adhesive chemistry to glass (and any second surface—metal, plastic).
- Define End Use: Interior display, exterior glazing, electronics assembly—each has different strength, clarity, and weathering demands.
- Choose Cure Speed and Method: Assess lamp type (UVA/UVB intensity), fixture geometry, and cycle time.
- Test and Validate: Conduct on-part testing for adhesion, accelerated aging, and safety (see ASTM D1002 or ISO 4587).
- Audit Compliance: Ensure MSDS/SDS, low VOC documentation, and regulatory reports are on file.
Key Performance Metrics for UV Glass Bonding Adhesives
The real-world performance of UV adhesives gets tested in both lab and production. Here are the benchmarks top manufacturers watch:
- Lap Shear Strength: >12 MPa (per ASTM D1002), required for structural glass assembly.
- T-Peel Strength: Indicates bond flexibility and shock resistance.
- Haze and Light Transmission: <1% haze for premium optical uses.
- UV Aging: No yellowing after 1,000 hours under 340 nm UV-A (accelerated test).
- Thermal Cycling: Bonds must survive -40°C to +85°C without loss of adhesion.
- Viscosity: cP range matters for bead, slot, and roll-coat dispensing.
- Pot Life and Open Time: Adequate work time before cure; cured instantly under UV, so careful timing is key.
Industrial Application Processes
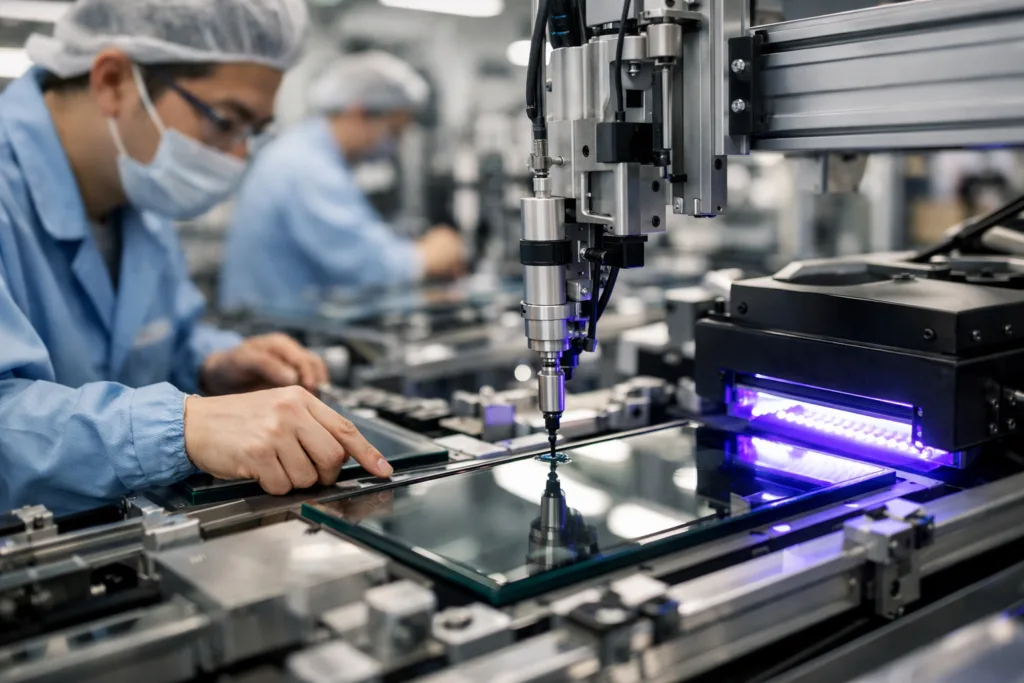
Process design shapes adhesive success as much as the chemistry. Best results come from automated, controlled dispensing—robotic bead application, slot-die systems for large panels, static mixers for dual-cure resins. UV lamps (LED or mercury) must match adhesive’s absorption for full cure. Clamping is needed to ensure thin, even bondlines.
Step-by-Step Guideline
- Clean and prep all bonding faces ( solvent degrease, dry lint-free wipe).
- Apply adhesive bead (<1 mm typical for close-tolerance glass). For larger gaps, increase layer with higher viscosity or thixotropic type.
- Align and clamp parts. Use spacers to control bondline thickness where clarity is critical.
- Expose bondline to appropriate UV wavelength and intensity. Cure times often range 2–30 seconds, depending on adhesive and lamp power.
- Perform quick quality checks—visual inspection for bubbles, haze, or uncured areas. Destructive peel test if needed.
- Store assembled parts as per technical data sheet; some dual-cure systems require post-heating or secondary UV exposure.
Quality and Compliance Considerations
Industry protocols require tracking batches for traceability, archiving all QC test data, and ensuring adhesives meet VOC and regulatory standards. ZDS provides full MSDS, ISO 9001 certification, and supports REACH/RoHS documentation for clients.
Best UV Adhesive for Glass
No single formula fits every scenario, but several ZDS and comparable industrial adhesives consistently outperform in glass bonding:
- ZDS UV-800 Series: High-strength, crystal-clear acrylic UV adhesives (lap shear up to 18 MPa; <1% haze). Outstanding for glass display assembly and decorative joints.
- ZDS Hybrid-EPOX UV-E100: UV/dual cure epoxy, for glass-to-metal bonding. Delivers superior chemical and water resistance.
- ZDS UV-MS Polymer S700: Flexible, elastic bonds for tempered and patterned glass. Excels in outdoor or expansion-prone environments.
Always arrange an application review with an adhesives specialist to fine-tune for your process and substrates. For tailored advice, ZDS technical teams can support sample bonding, custom formulation, and on-site trials through rapid prototyping.
FAQs: Best UV Adhesive for Glass Bonding
What defines the strength of a UV adhesive for glass?
Bond strength is measured in lap shear tests (ASTM D1002); industrial-grade UV adhesives achieve over 12 MPa, ensuring the assembly withstands stress and shock.
How do I ensure a UV adhesive remains clear over time?
Choose adhesives with proven UV resistance and stabilizers. High-quality products pass accelerated yellowing and haze tests, remaining colorless even after years of sunlight.
Can UV adhesives bond all types of glass?
Most UV adhesives suit clear and tempered glass, but low-E, coated, or laminated types may need specific formulations or surface primers for reliable adhesion.
What’s the typical cure time for UV glass adhesives?
Under the correct lamp (365–405 nm), UV adhesives cure in 2–30 seconds. Cure speed depends on layer thickness, lamp power, and adhesive formulation.
Is surface preparation required for glass bonding?
Yes, always clean surfaces with isopropanol and degrease. For best results on patterned or aged glass, gentle abrasion or a primer may help.
Are ZDS adhesives certified for industrial compliance?
ZDS adhesives provide full MSDS/SDS documentation, ISO 9001 quality, and regulatory support (REACH, RoHS, VOC) for global industrial use.