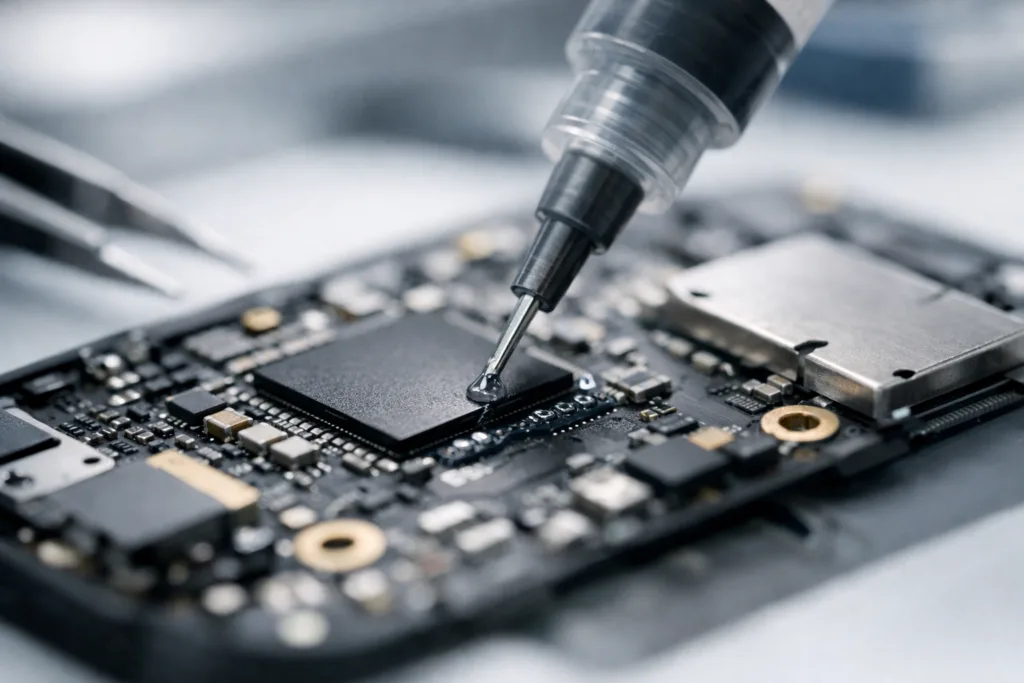
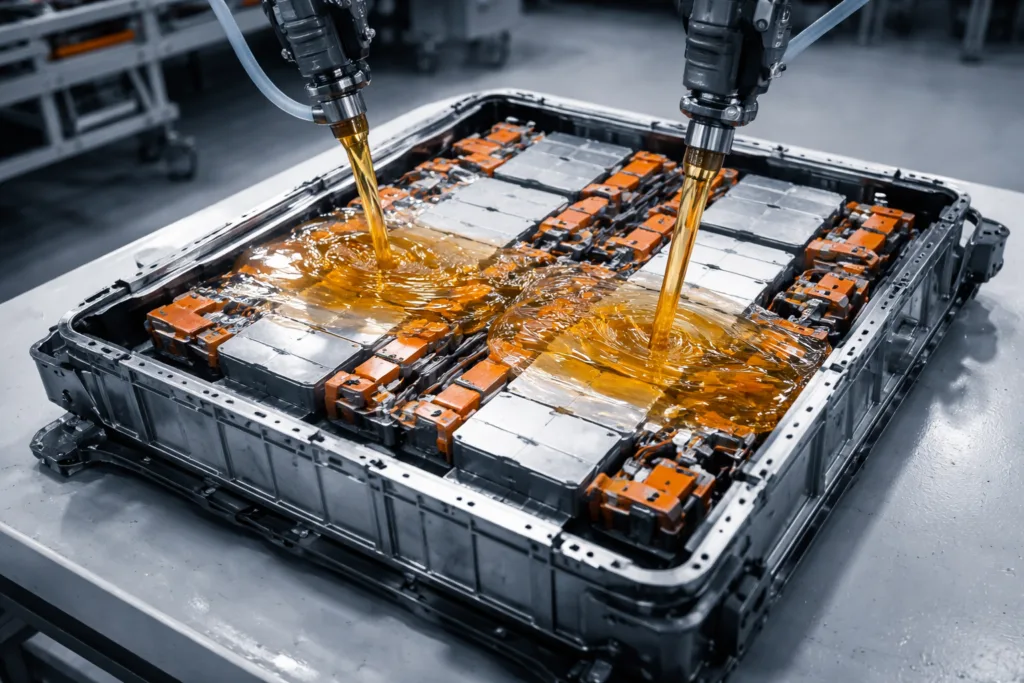
When choosing the right adhesive, the debate of cyanoacrylate vs epoxy is a common one. Both are widely used in various industries, but their chemical properties, strengths, and ideal applications differ significantly.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of these two glue types helps ensure optimal bonding performance. ZDS™ is a trusted adhesive manufacturer providing innovative bonding solutions tailored for structural and precision bonding applications.
What Is Cyanoacrylate Glue?
Cyanoacrylate adhesives, commonly known as “super glue,” are fast-acting adhesives that cure within seconds at room temperature. They work well on:
Advantages of Cyanoacrylate:
- Rapid curing without external heat
- High strength in small areas
- Minimal surface preparation
- Transparent bonding
Limitations:
- Brittle under stress
- Limited gap-filling ability
- Poor resistance to moisture and temperature extremes
What Is Epoxy Adhesive?
Epoxies are two-part structural adhesives that cure through a chemical reaction between resin and hardener. They form strong, durable bonds ideal for:
- Metals
- Composites
- Wood
- Concrete
Advantages of Epoxy:
- Exceptional strength and durability
- Good gap-filling properties
- Resistant to heat, chemicals, and moisture
- Long working time before curing
Limitations:
- Longer curing times (unless heat-accelerated)
- Requires precise mixing of components
- May need surface prep or primers
Adhesive Comparison: Cyanoacrylate vs Epoxy
| Feature | Cyanoacrylate | Epoxy |
|---|---|---|
| Cure Time | Seconds | Minutes to Hours |
| Strength | Moderate | High (Structural) |
| Flexibility | Low | Moderate to High |
| Gap-Filling | Low | Excellent |
| Moisture Resistance | Low | High |
| Heat Resistance | Low | High |
| Ease of Use | Very Easy | Moderate |
| Shelf Life | Short | Long (when unmixed) |
Which Structural Glue Should You Choose?
Use Cyanoacrylate When:
- Speed is essential
- The bond area is small and well-fitted
- The materials are low-stress and not exposed to moisture/heat
Use Epoxy When:
- Structural integrity is critical
- Materials require gap filling or will be exposed to harsh environments
- You can allow for longer cure times and surface prep
Real-World Application Scenarios
- Electronics: Cyanoacrylate for quick fixes; epoxy for encapsulation and long-term bonding.
- Automotive: Epoxy is preferred for structural components; cyanoacrylate for trims or interior parts.
- DIY and Crafts: Cyanoacrylate for speed; epoxy for durability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can cyanoacrylate be used as structural glue?
While it offers high bonding strength in small areas, it is not ideal for structural loads or harsh environments.
Is epoxy better than super glue for metal?
Yes, epoxy provides superior strength, especially when bonding metals subjected to mechanical stress or environmental exposure.
Are both adhesives permanent?
Both can form permanent bonds, but epoxy generally outperforms cyanoacrylate in long-term durability.
Conclusion: Choose Based on Application Needs
In the battle of cyanoacrylate vs epoxy, there’s no one-size-fits-all answer. For quick, precision bonding, cyanoacrylate is excellent. For heavy-duty, reliable performance, epoxy is the better structural glue. Work with industry experts like ZDS™ to determine the best solution for your specific bonding challenge.