Understanding Dielectric Strength in High-Voltage Battery Potting
Dielectric strength is a vital property for materials used in high-voltage battery potting. In electric vehicle (EV) and energy storage systems, battery modules operate at high voltages and must be protected from electrical failures. Dielectric strength requirements for high-voltage battery potting refer to the ability of a potting compound to resist electrical breakdown—crucial for ensuring safe, long-lasting insulation and reliable battery performance.
Let’s take a closer look at why dielectric strength matters, how it’s measured, and how engineers can select materials that meet demanding electrical protection standards.
What Is Dielectric Strength and Why Does It Matter?
Dielectric strength refers to the maximum electric field a material can withstand without breaking down or conducting electricity. For battery potting, high dielectric strength means better insulation and reduced risk of short-circuits or thermal runaway. High-voltage applications demand materials that can block electric current even under stress, voltage spikes, or harsh operating conditions.
| Material | Typical Dielectric Strength (kV/mm) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | 15–30 | Battery pack encapsulation |
| Polyurethane | 18–30 | Flexible battery modules |
| Silicone | 20–35 | High-temperature batteries |
Inadequate dielectric strength means potential electrical breakdown, safety hazards, and shortened battery lifespan. That’s why industry experts, including manufacturers like ZDS Adhesive, emphasize rigorous testing and material selection.
How Dielectric Strength Affects Battery Safety and Longevity
Effective insulation is not just about ticking boxes—it’s about protecting people and technology. Here’s how proper dielectric strength impacts real-world battery systems:
- Prevents short-circuits: Strong insulation stops unintended current flow between cell terminals.
- Stops thermal runaway: Prevents dangerous overheating and fire risk.
- Extends battery life: Reduces degradation from electrical stress and moisture ingress.
- Complies with safety standards: Meets critical certifications such as UL94 V-0 for flame retardancy.
Real-World Failures Caused by Poor Dielectric Strength
Case studies show that poorly potted batteries with low dielectric strength can lead to catastrophic failures. For instance, a 2025 EV recall highlighted modules where potting resin failed under high humidity, causing cell shorting and fires. These real-world scenarios highlight the importance of rigorous selection and process control.
Industry Standards for Evaluating Dielectric Strength
Key standards guide how dielectric strength should be measured:
- ASTM D149 – Standard method for testing dielectric breakdown voltage.
- IEC 60243 – Specifies dielectric strength testing for insulating materials.
- UL94 V-0 – Evaluates flammability: essential for battery safety.
These standards involve placing a sample between two electrodes and gradually increasing voltage until breakdown occurs.
Testing Methods for Dielectric Strength
- Breakdown test: Measures the voltage at which failure occurs.
- Step-up method: Gradually increases voltage to assess insulation margin.
- Environmental simulation: Includes humidity, temperature, and contamination.
Producers like polyurethane potting glue manufacturers routinely use these standards in lab and pilot lines.
Choosing Potting Materials That Meet Dielectric Strength Requirements
Material Selection Criteria
- Voltage rating: Should exceed max system voltage plus safety margin.
- Chemical compatibility: Must resist electrolyte leakage and contaminants.
- Thermal stability: Must maintain integrity over wide temperatures.
- Moisture resistance: Low water absorption to maintain insulation over time.
For example, high-performance epoxy potting compounds, like those listed on ZDS Adhesive’s product page, offer superior dielectric properties for demanding battery applications.
Evaluating Polyurethane Versus Epoxy and Silicone
| Property | Epoxy | Polyurethane | Silicone |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Strength | High | High | Very High |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Excellent | Good |
| Thermal Stability | Very Good | Good | Best |
| Water Resistance | Moderate | Excellent | Excellent |
Engineers must balance dielectric strength with processing and end-use requirements.
Real-World Applications: High-Voltage Battery Potting in Action
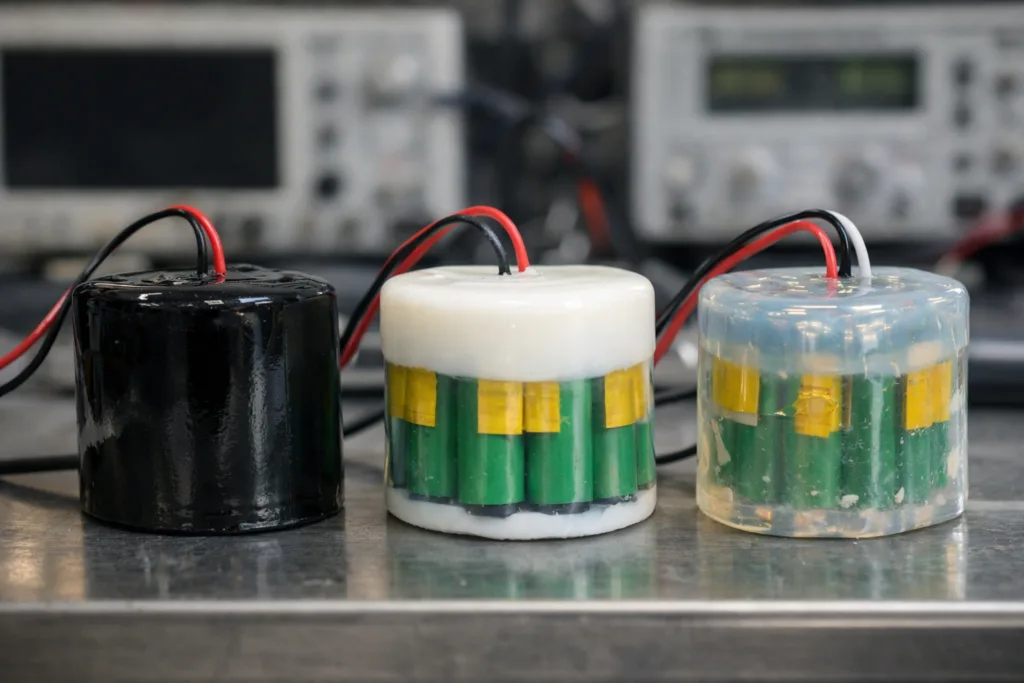
In electric vehicles and grid storage, battery modules are exposed to wide temperature swings, vibration, and voltage surges. Designs often require customized potting recipes to guarantee that insulation stays strong over 5–10 years of service.
Case Study: EV Battery Module Potting
In a recent EV module project, engineers selected a two-part polyurethane compound with dielectric strength tested at 29 kV/mm. Continuous thermal cycling and humidity aging were performed, showing the potting material kept its properties with minimal loss over three years. Battery packs passed UL94 V-0 and IEC 60243 type testing, exceeding customer reliability targets.
Consequences of Inadequate Dielectric Strength in Battery Potting
Using a potting material with subpar dielectric properties can lead to several risks:
- Electrical arcing between cells, risking fire and heat damage.
- Accelerated component failure due to moisture ingress and creepage.
- Warranty claims and recalls—as seen in European EV launches in 2024–25.
- Non-compliance with certification standards, causing project delays.
Mitigating Risks: Best Practices for High-Voltage Battery Potting
Engineering-Led Material Evaluation
- Demand independent certification of dielectric strength for each lot.
- Simulate worst-case conditions (high humidity, voltage surges).
- Review chemical compatibility with battery electrolytes.
From an assembly-line viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, best practice includes lap shear, peel, and humidity aging tests alongside dielectric strength checks to prevent surprises in production runs. Substrate pretreatment (plasma, primer) further improves insulation margins and bond reliability.
Practical Steps for Insulation Performance
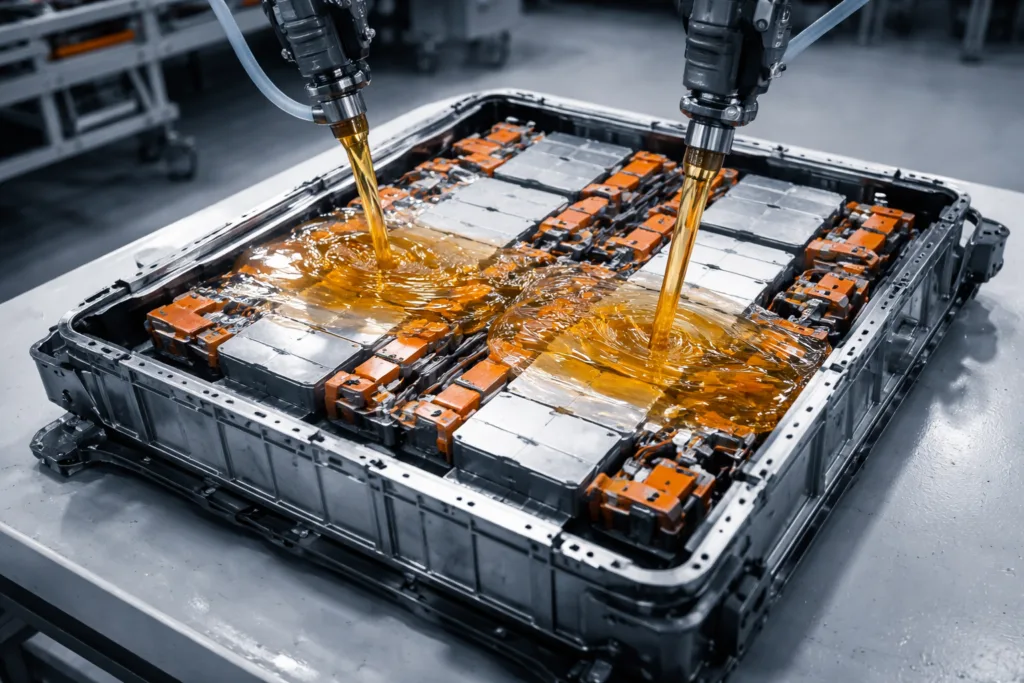
- Apply potting compounds evenly to avoid voids (which cause breakdown).
- Control cure schedules so material reaches its full electrical property set.
- Use test coupons in every batch to track consistency.
Dielectric Strength Requirements for High-Voltage Battery Potting
The specific dielectric strength target for high-voltage battery potting depends on system voltage. For example:
- EV Modules (400–800 V): Minimum 18–30 kV/mm
- Grid Storage (1000–1500 V): Minimum 25–35 kV/mm
Material selection and in-line testing must always factor in voltage spikes and long-term aging. When in doubt, engineers should aim for a margin above predicted stress levels, as field failures often stem from underestimating environmental or real-world voltage risks.
Innovations in Potting Compounds for Battery Insulation
Recent advances include nano-filled epoxy and silicone formulations that push dielectric strength higher while retaining flexibility and thermal management properties. Some compounds now combine UL94 V-0 fire resistance and self-healing features.
Nano-Fillers and Enhanced Thermal Management
Nano-fillers improve the electrical barrier and boost heat dissipation—important for batteries with high power density. These innovations further reduce risk and extend battery life.
Practical Observations: Field vs. Lab Dielectric Strength
Lab ratings can differ from field performance due to aging, contamination, and processing variations. That’s why regular batch testing and tight material controls are required. Field engineers should look for robust test data at both ambient and elevated temperatures.
Selecting and Validating Potting Compounds
Validation Checklist
- Confirm supplier data with independent lab tests.
- Include accelerated aging and humidity testing.
- Monitor variance across production lots.
- Update process controls whenever new battery chemistries are introduced.
Ultimately, strong dielectric strength is only as good as the end-to-end process—from receiving material to final cure in production modules.
Conclusion: Delivering Safe, Reliable Battery Systems with Proper Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength is at the heart of battery safety, system reliability, and regulatory compliance in any high-voltage application. From material selection through validation and process control, every step counts. Manufacturers who invest in rigorous testing, proven potting compounds, and robust engineering standards will continue to lead in delivering safe, dependable energy storage solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dielectric strength and how is it measured?
Dielectric strength is the maximum electric field a material can withstand without electrical breakdown. It’s measured by applying a ramped voltage across a sample until failure, often using test methods like ASTM D149.
Why is dielectric strength critical in battery potting?
High dielectric strength ensures strong insulation, protecting against short-circuits, fire risks, and improving battery longevity. It’s crucial for high-voltage safety.
How do environmental conditions affect dielectric strength?
Humidity, extreme temperatures, and contamination can reduce insulation performance over time. That’s why materials must be tested under simulated real-world conditions.
Are there industry standards for minimum dielectric strength?
Yes. Standards like IEC 60243 and UL94 V-0 specify minimum requirements to ensure safety and reliability, with typical targets ranging between 18–35 kV/mm depending on voltage.
Can adding fillers or changing chemistry improve dielectric strength?
Yes. Innovations such as nano-fillers can boost dielectric performance and enhance thermal management, helping materials perform reliably in harsh environments.
How often should dielectric strength be tested in production?
Testing should occur with every production batch, including accelerated aging and environmental simulation tests, to track consistency and prevent field failures.
Related Reading
- Silicone vs Polyurethane: Which Is Best for Battery Modules?
- How Nano-Fillers Boost Thermal Management in Epoxies
- Keeping Batteries Safe: UL94 V-0 Solutions Against Thermal Runaway
- Mastering Adhesive Selection for EV Battery Cooling Plates
- How Water Absorption Impacts Epoxy Insulation: Insights for Engineers