Introduction: How to Bond Carbon Fiber to Aluminum (Dissimilar Materials Guide)
Carbon fiber and aluminum are both stars in modern engineering, bringing strength and lightness to industries like automotive and aerospace. But joining them? That’s a real materials challenge. If you’ve ever wondered about how to bond carbon fiber to aluminum (dissimilar materials guide), you’re not alone. This article explores why these advanced materials are difficult to combine, the specialized adhesives needed, surface preparation secrets, and real-world tips for maximizing bond performance in production.
Why Bond Carbon Fiber to Aluminum?

Designers often use carbon fiber and aluminum together to create light yet strong structures. Products from electric car body panels to aircraft control surfaces benefit from their distinct properties. But their chemical and physical differences make bonding tricky. Understanding the “why” sets a strong foundation before you pick your adhesives or tools.
Common Challenges in Carbon Fiber and Aluminum Bonding
Bonding carbon fiber to aluminum isn’t simple. Their surfaces have different energies, making it hard for adhesives to “wet” or stick. Carbon fiber is often coated with resin, while aluminum naturally forms an oxide layer. These must be addressed to prevent weak or unreliable joins. Furthermore, their expansion rates differ, risking bond failure under temperature changes. Managing these challenges is the key to success.
Key Applications in Automotive and Aerospace
The combination of carbon fiber and aluminum appears in:
- Automotive structural reinforcement (EV bodies, crash beams)
- Aerospace components (wing spars, fuselage parts)
- Sporting goods (bike frames, racing gear)
Here, bond integrity is paramount for safety and performance.
Adhesive Selection Criteria for Dissimilar Materials
The right adhesive must bridge the differences between carbon fiber’s rigidity and aluminum’s flexibility. You’ll want superior lap shear and peel strength, tolerance to moist and thermal cycling, and often a quick fixture time for assembly. Industrial adhesives tailored for structural bonding are frequently used for this purpose.
Types of Adhesives Used for Carbon Fiber to Aluminum
Several adhesive chemistries are up for the task:
- Epoxy Adhesives: High strength, great environmental resistance. Widely used in aerospace.
- Acrylic Structural Adhesives: Quick fixture, forgiving on surface prep, good impact strength.
- Polyurethane Adhesives: Flexible, absorb vibration, and tolerate thermal cycling.
- Cyanoacrylate (“Super Glue”): Useful for small or temporary bonds, but limited flexibility.
Choosing among them means weighing open time, cure methods, gap-filling ability, and the load type expected in application. Explore options with a trusted manufacturer of acrylic structural adhesives to match your project’s specific needs.
Surface Preparation: The Foundation of a Strong Bond
Preparation is everything. Poorly prepped surfaces undermine the strongest adhesive. Both materials require different approaches:
- Aluminum: Remove oxide layer using abrasion (sanding, brushing), chemical etching, or plasma treatment.
- Carbon Fiber: Slight abrasion, followed by solvent wipe (acetone, isopropyl alcohol), and drying.
This creates a rough, clean surface for maximum adhesive grip.
Surface Treatment Methods for Aluminum and Carbon Fiber
Going beyond basic cleaning, some applications demand:
- Plasma or Corona Treatment: Raises surface energy of carbon fiber for better wetting.
- Primers: Special primers can bridge adhesion for low-energy substrates or challenging alloys.
- Adhesion Promoters: Enhance chemical bonding at the interface.
The right surface treatment can double or triple bond strength, especially in harsh environments.
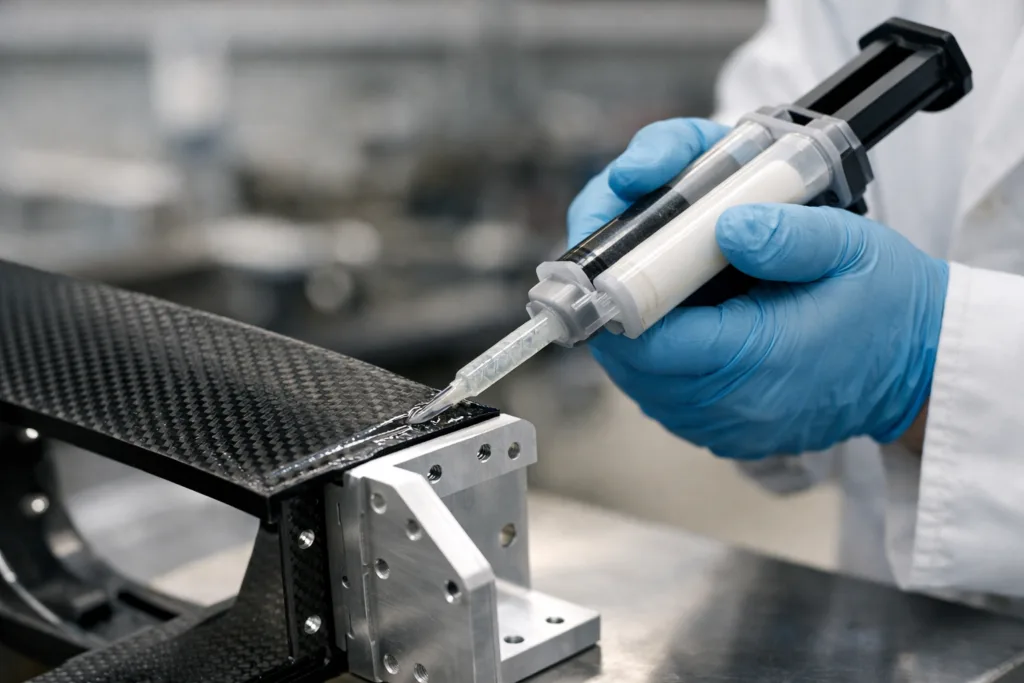
Step-by-Step Bonding Process
While details depend on your adhesive’s datasheet, a standard workflow is:
- Clean both surfaces with solvent and a lint-free cloth.
- Abrade (sand) the aluminum lightly; do the same (carefully) to resin-coated carbon fiber.
- Apply primer or adhesion promoter if needed.
- Dispense adhesive in a consistent, moderate layer (typically 0.1–0.5 mm bond-line).
- Mate parts and apply uniform pressure. Use clamps or fixtures as recommended.
- Cure per the adhesive’s instructions—room temp, elevated, or UV, depending on chemistry.
Always verify with small test panels before scaling up.
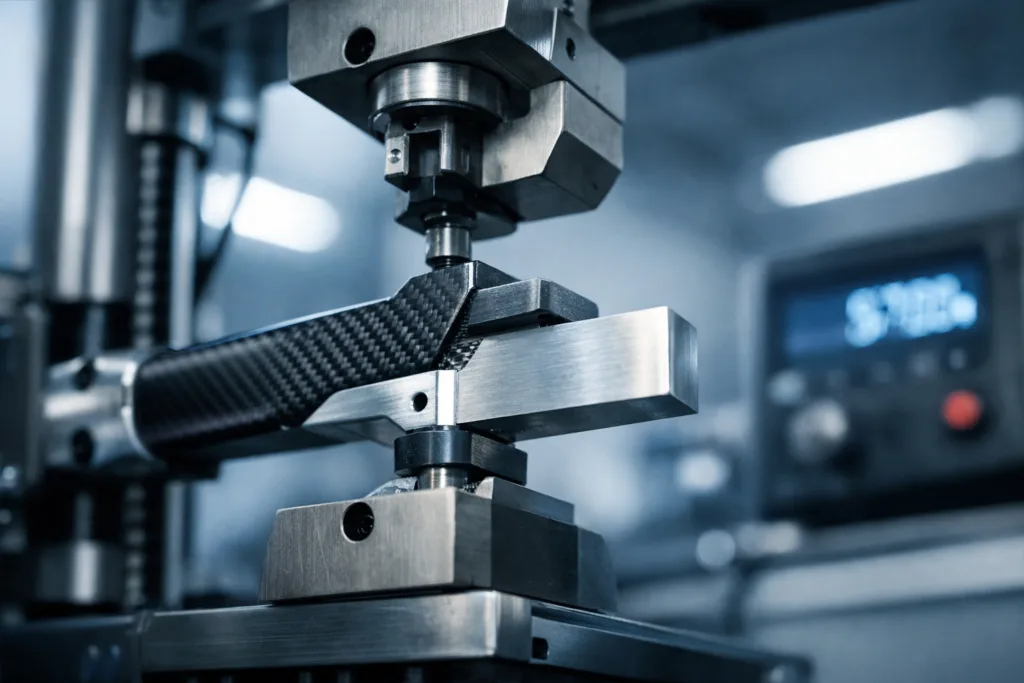
Testing Bond Strength: Techniques and Best Practices
Testing is crucial for high-reliability applications. Use lap shear, peel, and thermal cycling tests to evaluate real-world performance. For industrial consistency, many teams rely on test data to refine surface prep and adhesive choice. Guidelines on how to approach this can be found in best practices for improving adhesive strength.
Environmental Factors and Durability
Environmental exposure—humidity, salt, heat, and cold—can challenge even the strongest bonds. Use adhesives rated for your environment, and don’t skip process controls. Sealing the bond’s edge adds another layer of defense against corrosion and moisture intrusion.
Adhesive Curing Mechanisms: Heat, UV, and Room Temperature
Choose a cure mechanism that fits your throughput and substrate. Room-temperature curing is user-friendly, but heat-curable systems allow faster strength build-up and may raise performance. UV-curing adhesives are rarely used for totally opaque assemblies, but hybrid parts are sometimes primed with UV systems before a structural bond.
Common Bonding Failures and How to Prevent Them
- Poor surface prep (trapped oils or oxide layers cause interface failures)
- Improper adhesive selection (rigid vs. flexible, or lack of thermal endurance)
- Insufficient pressure during cure (voids or air pockets in the bond-line)
Careful process control addresses most failures before they reach the test bench—or the field!
Comparison Table: Adhesive Selection Matrix
| Adhesive Type | Strength | Flexibility | Cure Time | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy | High | Medium | 30 min – 24 hr | Aerospace/Automotive structures |
| Acrylic | High | Good | 5–20 min | Large assemblies, varied surface prep |
| Polyurethane | Medium | Excellent | 30 min – 2 hr | Vibration, flexible joints |
| Cyanoacrylate | Medium | Poor | Seconds | Temporary/small fixes |
Industry Insights: ZDS Adhesive’s Approach
From the application engineer’s viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, selecting the right adhesive for carbon fiber to aluminum bonds boils down to three check-points: proper surface energy, appropriate open time and fixture time, and testing under expected temperature swings. For high-volume or safety-critical parts, a combination of primer, plasma treatment, and a two-part structural adhesive delivers the most reliable results. Testing with lap shear and humidity cycling is a must.
Automotive Use Case: EV Battery Chassis Assembly
Carbon fiber’s rigidity complements aluminum’s lightness in EV battery supports. Manufacturers use polyurethane or modified epoxy adhesives that tolerate vibration and expansion, often reinforced with mechanical fasteners for redundancy. For these applications, automotive bonding solutions address requirements for fast cycle times, regulatory compliance, and longevity.
Aerospace Example: Fuselage and Wing Joints
In aerospace, every gram counts but every joint must survive years of cycles. Epoxy adhesives tailored for aerospace ensure remarkable peel and lap shear strength and, when combined with surface treatments and controlled cure, exceed industry standards for fatigue and durability.
Testing and Quality Control Best Practices
Continuous improvement means regularly pulling bond samples, running environmental simulations, and documenting failures. Use digital monitoring wherever possible to track batch-to-batch consistency. Teams that foster this culture of vigilance avoid the most costly warranty and recall issues.
Advanced Adhesive Technologies on the Horizon
New nano-fillers, hybrid cure mechanisms, and tunable flexibility are being integrated into next-generation adhesives as demands increase. Stay informed—process updates could unlock greater design freedom or cost efficiency. Find more in our related posts below.
How to Bond Carbon Fiber to Aluminum (Dissimilar Materials Guide)
To sum up, how to bond carbon fiber to aluminum (dissimilar materials guide) comes down to understanding each material, selecting a compatible adhesive system, and executing consistent surface preparation. Test thoroughly, adapt your process, and let reliability drive your choices—no shortcuts. The latest adhesive solutions now make it possible to achieve bonds as strong as either material alone, unlocking new designs for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best adhesive for bonding carbon fiber to aluminum?
Epoxy adhesives are generally considered the strongest, but acrylic and polyurethane adhesives can sometimes offer better flexibility and tolerance to cycling. Always match your adhesive to your specific application and environment.
How do you prepare aluminum for bonding to carbon fiber?
Abrade the surface lightly, clean with a solvent, and remove oxide layers. In some cases, a primer or plasma treatment is recommended to increase surface energy for better adhesion.
Can you use cyanoacrylate (super glue) for large or load-bearing joints?
Cyanoacrylate is generally not recommended for structural or high-load bonds, as it is brittle and lacks long-term durability compared to epoxy or polyurethane adhesives.
Do you need to use both mechanical and adhesive joining methods?
For high-safety applications, combining adhesives with rivets or fasteners provides redundancy and enhanced fatigue resistance, especially in automotive and aerospace structures.
How do you test if the bond is working correctly?
Run lap shear and peel strength tests, check for cohesive failure modes, and simulate thermal and humidity cycles to ensure the bond can survive all expected conditions.
What issues commonly cause bond failures between carbon fiber and aluminum?
Poor surface preparation, incorrect adhesive selection, and improper curing are leading causes. Following all steps and standards is vital to avoid premature failure.
Related Reading
- Why Structural Adhesives Outperform Welding in Aluminum Car Assemblies
- How Toughened Epoxies Raise Metal Bonding Reliability in 2026
- Selecting the Right Adhesive for Metal-to-Metal Bonding: Benefits and Pitfalls
- Preventing Common Adhesive Failures: Pro Strategies Explained
- Choosing Thermal Conductive Adhesives for Modern EV Battery Packs