Understanding Industrial Adhesives for Automotive Manufacturing
Modern cars rely on more than nuts and bolts. Industrial adhesives have become essential in automotive manufacturing, joining parts from headlights to dashboard panels. Right adhesive selection shapes car safety, comfort, and even style.
Automotive Adhesive Applications: Where Bonding Matters Most
Automotive adhesive needs vary across different parts. Every bonding point in a vehicle faces its own special challenges—from vibrations and impacts to heat and chemical exposure. Car makers now use adhesives for:
- Headlamps and lighting units: Joining plastics, glass, and metals with watertight, flexible bonds.
- Interior assemblies: Gluing trim, instrument panels, and displays for quiet, rattle-free cabins.
- Battery packs and electronics: Insulating and protecting electric vehicle (EV) circuitry, cells, and modules.
- Structural and panel bonding: Reinforcing body panels, frames, and closures under crash and vibration loads.
Understanding each environment ensures long-lasting performance.
Challenges in Automotive Bonding: From Heat to Vibration
Automotive adhesives face tough demands. Each joint must survive mechanical stress, temperature swings, humidity, and road chemicals.
- Vibration loads: Cars travel bumpy roads. Bonds must flex but not crack or peel.
- Temperature extremes: Engine bays, lamp housings, and EV batteries heat up fast. Adhesives must stay stable from −40°C to over 120°C (−40°F to 248°F).
- Chemical resistance: Road salt, oil, and cleaning fluids reach every surface. Only chemical-resistant adhesives withstand these attacks.
- Lightweighting: Car makers use more engineered plastics and composites. Gluing unlike materials demands specialty adhesives, surface prep, and primers.
Top adhesives also need fast cure speeds, simple application, and consistent results under high-volume manufacturing conditions. That’s why automotive-grade adhesives are tested following international standards—such as ASTM D1002 lap-shear for bond strength and B117 salt spray for corrosion.
Types of Industrial Adhesives Used in Automotive Manufacturing
Adhesives for cars come in many chemical systems, each with specific benefits. Popular options include:
| Chemistry | Main Substrates | Key Properties | Common Automotive Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy (1K/2K) | Metals, plastics, glass | High strength, good heat resistance, gap fill | Body panels, structural bonding, battery cells |
| Polyurethane (PU) | Plastics, composites, metals | Flexibility, vibration resistance, fast cure | Windshields, headlamps, roof modules |
| Acrylic | Metals, plastics, composites | Impact resistance, fast fixturing, tough bonds | Trim, emblems, crash structures |
| Silicone | Glass, metal, electronics | UV, temperature tolerance, sealant | Lamps, EV electronics, weathersealing |
| Cyanoacrylate (CA) | Plastics, rubber, metal (small areas) | Ultra-fast cure, spot bonding | Sensors, connectors, dash assembly |
| MS Polymer/Hybrid | Multipurpose: metals, glass, plastics | Medium strength, flexibility, primerless | Seals, body shop, trim |
| Tape/Film | Plastics, metals, glass | Die-cut, quick process, clean application | Badges, displays, interior trims |
Single-Component or Two-Part?
Single-component (1K) adhesives simplify dispensing—one cartridge, no mixing. Two-component (2K) adhesives offer higher strength, but require careful mixing and cure control. The choice depends on process speed, bond strength, and part geometry.
How Cure Mechanism Impacts Production
Adhesives cure by moisture, heat, UV, or mixing. Rapid UV-curable adhesives are growing for lamps and electronics. Heat-cured epoxies deliver unmatched stability for engine and battery assembly. Moisture and room temperature (RT) cure polyurethanes speed up body shop lines.
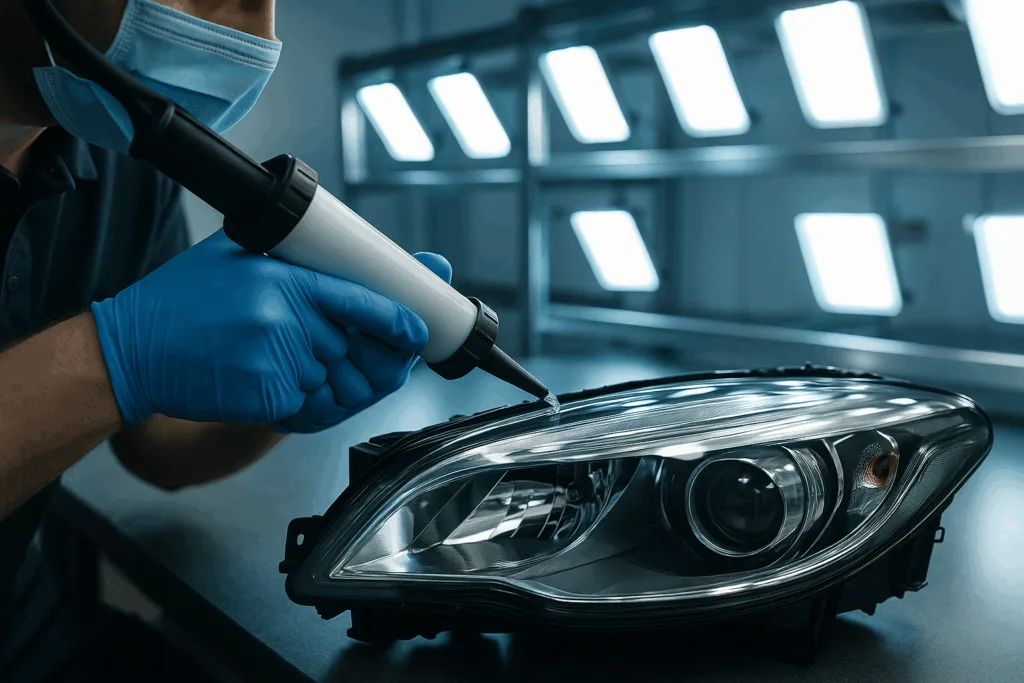
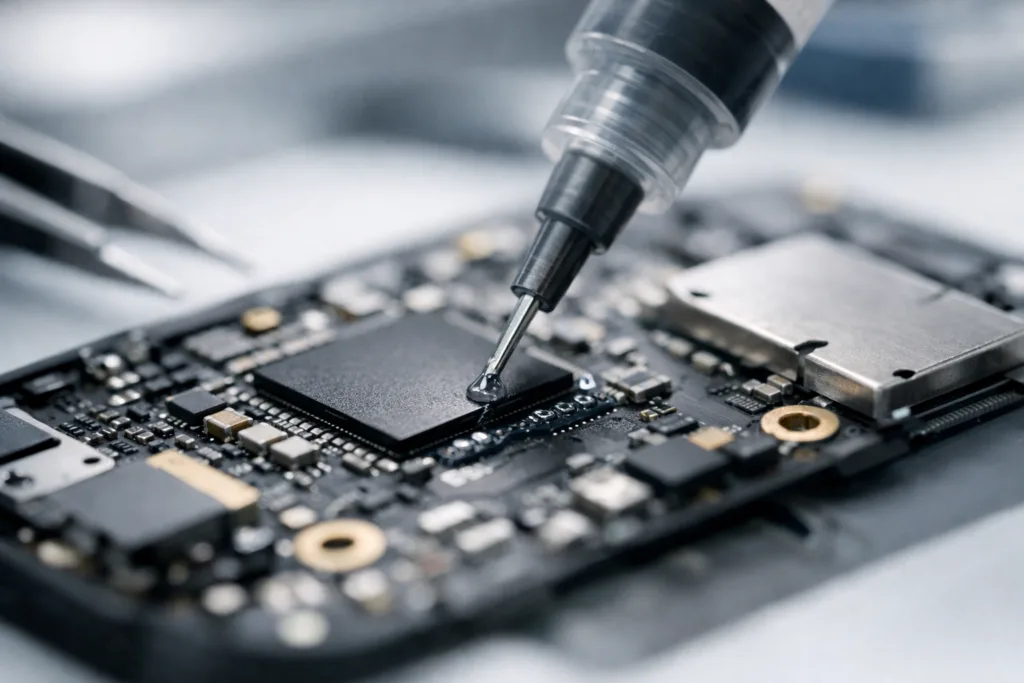
Lighting and Headlamp Bonding: Clarity and Security
Automotive lighting units combine clear plastics, reflectors, and electronics. These assemblies face UV light, heat, and water ingress. Headlamp adhesive must flow smoothly for automated bead dispensing. Once cured, it forms a tough, flexible joint. This joint holds lens to housing—even when driving over rough roads or in extreme weather. High-end lamps, such as LED or matrix beam systems, need adhesives with low outgassing to prevent fogging.
- Best chemistries: 2K polyurethane, UV-curable silicone, toughened acrylic
- ZDS recommendation: Use a moisture-cure PU for water-tight edge sealing and a fast-curing UV adhesive for lens bonding on automated lines.
Application Tips
- Clean parts: Remove dust, release agents, or oils from plastics and metal surfaces
- Automated application: Choose adhesives with consistent viscosity (cP) for robot dispensing
- Proper cure: Maintain UV intensity or fixture heat per manufacturer specs
Adhesives for Automotive Interiors: Quiet, Comfort, and Safety
Todays cars offer comfortable, quiet cabins with sleek finishes. Adhesive for car parts in interiors bonds plastics, leather, fabrics, and wood trims. The chosen adhesive must stay strong but flexible, handle temperature shifts, and stay nearly invisible.
- Headliner bonding
- Instrument panel assembly
- Display and touchscreen integration
- Airbag cover attachment
Low-odor, non-yellowing cyanoacrylate or fast-fixturing acrylics work well for displays and trim. Water-based PU and hot-melt systems give strong, eco-friendly results for large panels.
Pain Points and Solutions
- Rattle and Squeak Prevention: Flexible adhesives (Shore A 20–60) absorb vibration and create a tight fit.
- Flame Retardancy: Interior adhesives must often meet flammability standards (e.g., FMVSS 302).
- Speed: Fast grab and quick fixture times matter for automated or manual production.
ZDS can advise on suitable adhesives for dashboards and delicate trim parts, balancing speed with cosmetic quality.
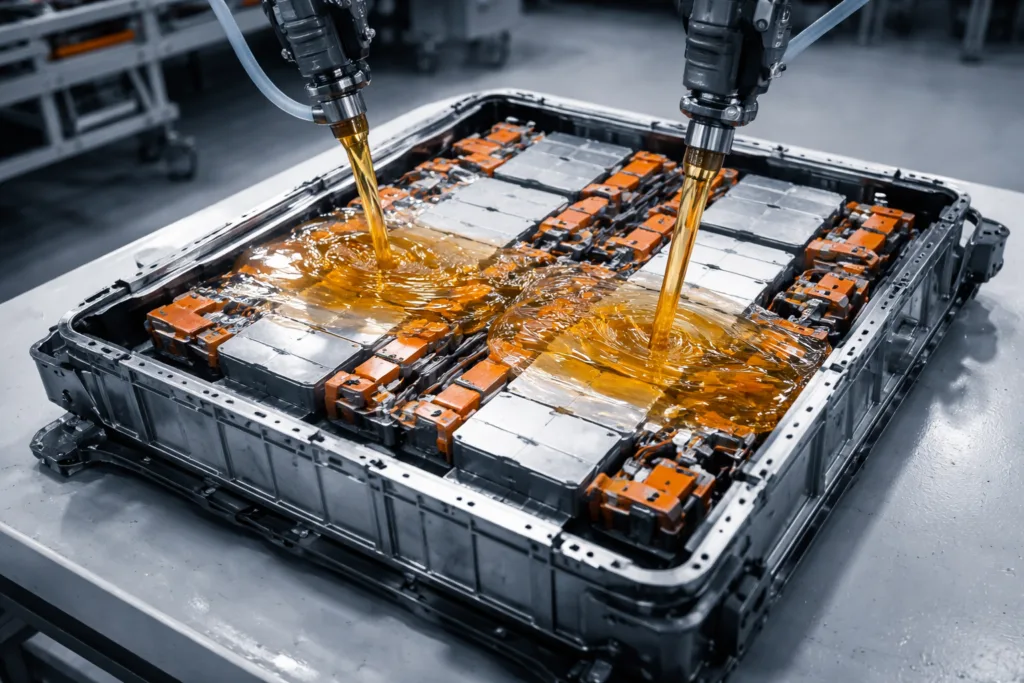
Battery Pack Assembly and EV Applications: Safety First
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) quickly changes the automotive adhesive landscape. Battery packs demand insulating, thermally conductive, and fire-resistant adhesives. Bonds must survive high-voltage currents, wide temperature swings, and even impacts. Thermal management and vibration reduction protect battery health.
- Cell-to-cell gluing for shock absorption and insulation
- Module and casing assembly for leak-proof seals
- Thermal interface materials (TIMs) for heat dissipation
Epoxy adhesives—chosen for precise mix ratios and high glass transition temperature (Tg)—provide strong, durable results. Silicone and acrylic options insulate electronics while allowing for thermal movement.
Expert takeaway: Apply adhesive under clean-room conditions when possible. Test each bond with salt spray (ASTM B117) and thermal cycling to ensure safe EV operation.
ZDS adhesive supplies high-purity, low-outgassing adhesives ideal for battery pack and EV electronics assembly.
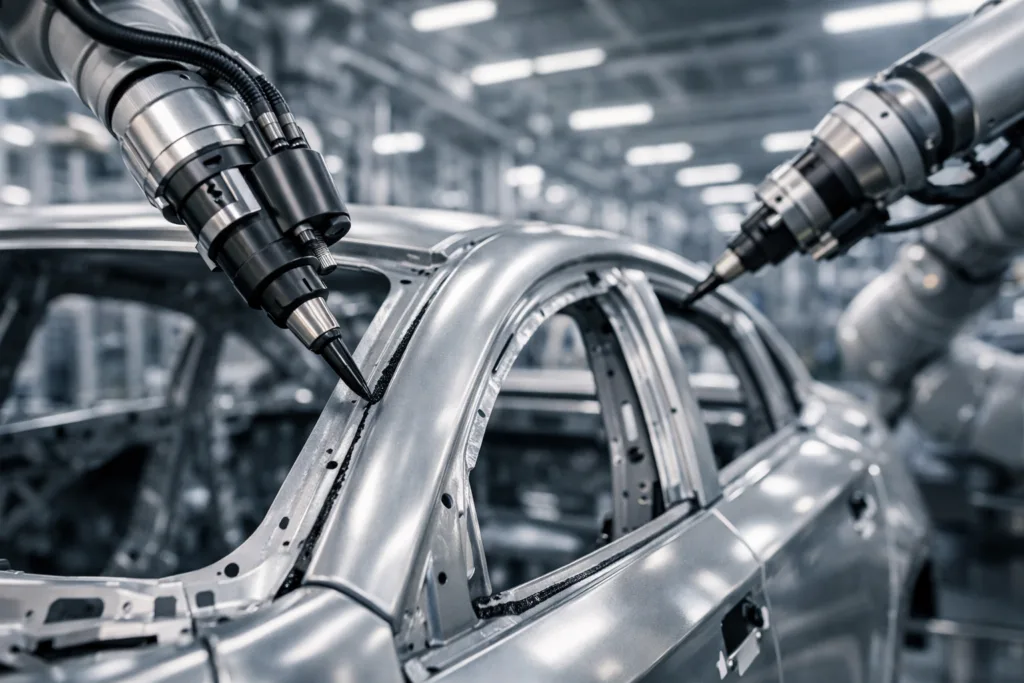
Structural Bonding: Lightweight Strength for Body and Chassis
Structural bonding refers to joining major load-bearing parts, such as frames and panels. This method replaces some spot welding or mechanical fasteners. The advantages include:
- Reduced vehicle weight for better fuel efficiency
- Improved crash energy absorption
- Corrosion prevention by sealing joints
Automotive adhesives for these joints must reach lap shear strengths above 20 MPa, resist fatigue, and stay tough over time. Two-part epoxies and acrylics, often applied by bead or slot-die, are standard.
Best Practices for Structural Bonding
- Prepare surfaces: Abrade and clean metals, use primers on composites/engineered plastics.
- Controlled dispensing: Use static mixers for consistent 2K application.
- Clamping: Enforce consistent pressure during cure.
Proven adhesives and controlled processes mean fewer recalls and safer vehicles.
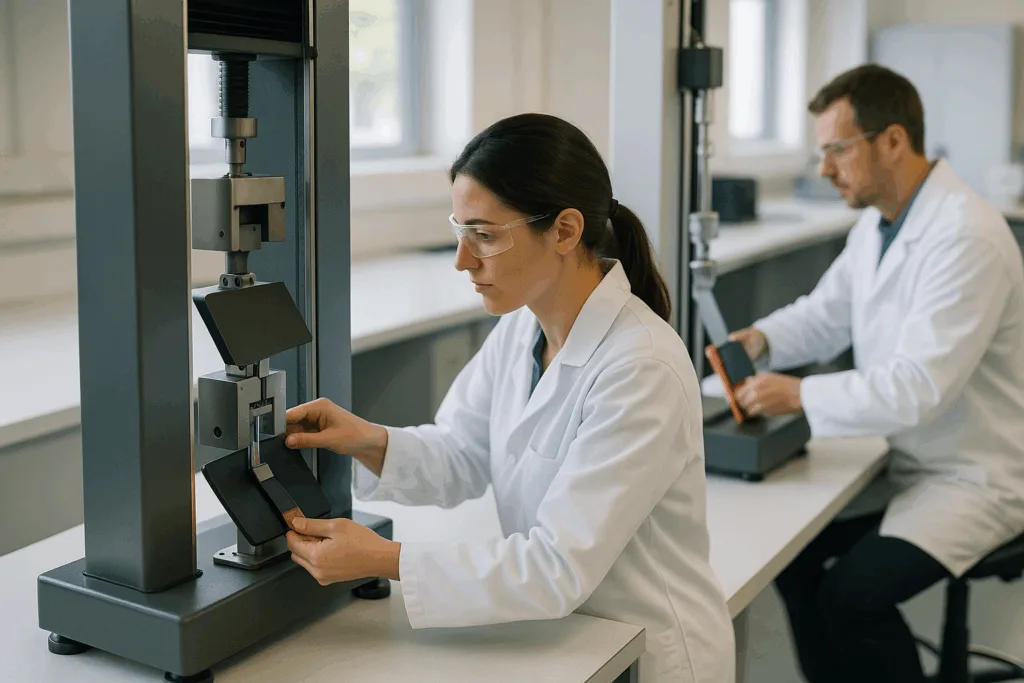
Process Control and Quality Assurance in Adhesive Application
Ensuring long-term bond performance requires careful process control. Automotive standards demand tight tracking and validation at every step:
- Material traceability: Each adhesive batch logged for auditing and recalls
- Process monitoring: Temperature, mix ratios, and dispense rates must stay within spec
- Testing: Pull, shear, and peel tests validate each joint (ASTM D1002, D1876)
- Compliance: Meets REACH, RoHS, low-VOC requirements for worker and vehicle safety
Documentation and Logistics
ZDS provides up-to-date SDS, technical data sheets, and ISO 9001 manufacturing lots for peace of mind and regulatory compliance.
Surface Preparation: The Key to Reliable Bonding
The best adhesive for car parts is only as good as its surface preparation. Metals need degreasing, light grit-blasting, or abrading. Plastics may require corona or plasma treatment, or special primers for low-surface-energy types (like PP or PE). Consistent cleaning ensures repeatable bonds and avoids costly failures.
- Wipe with recommended cleaners
- Test for water-break (no beading) to confirm surface readiness
- Apply primers for glass, composites, or hard-to-bond plastics
Run small-scale tests with the chosen adhesive and process before scaling up to full production.
Automotive Adhesive: Selection and Supplier Guidance
Selecting the right adhesive balances strength, speed, cost, application fit, and compliance. Review your bonding needs with an experienced technical supplier, like ZDS, who knows the full range of epoxy, PU, silicone, MS Polymer, and tape-based solutions. Share your requirements for cycle time, automation level, substrates, and performance targets. That ensures better results, less downtime, and safer cars.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the best adhesive for car headlamp bonding?
Two-part polyurethane or UV-curable silicone adhesives deliver watertight, flexible bonds for headlamp assemblies, handling heat and vibration well.
How do I select an adhesive for bonding automotive interior trim?
Choose flexible, low-odor adhesives—such as water-based PU or fast-fixturing acrylics—to bond plastics, fabrics, and wood inside the cabin.
Are automotive adhesives suitable for bonding plastics and metals together?
Yes, specialized epoxies, acrylics, and hybrid MS adhesives bond metals to plastics, provided surfaces are properly cleaned and primers are used if needed.
What testing ensures adhesive durability in automotive manufacturing?
Key tests include lap shear (ASTM D1002), T-peel (ASTM D1876), and environmental aging like salt spray (ASTM B117) and thermal cycling.
Why use adhesives instead of welding or fasteners in cars?
Adhesives reduce weight, prevent corrosion, spread loads evenly, and enable joining of non-weldable materials, improving performance and design options.
How important is surface preparation for adhesive success?
Proper cleaning and treating of surfaces is critical—poor prep leads to weak bonds and possible failures, even with the best automotive adhesives.