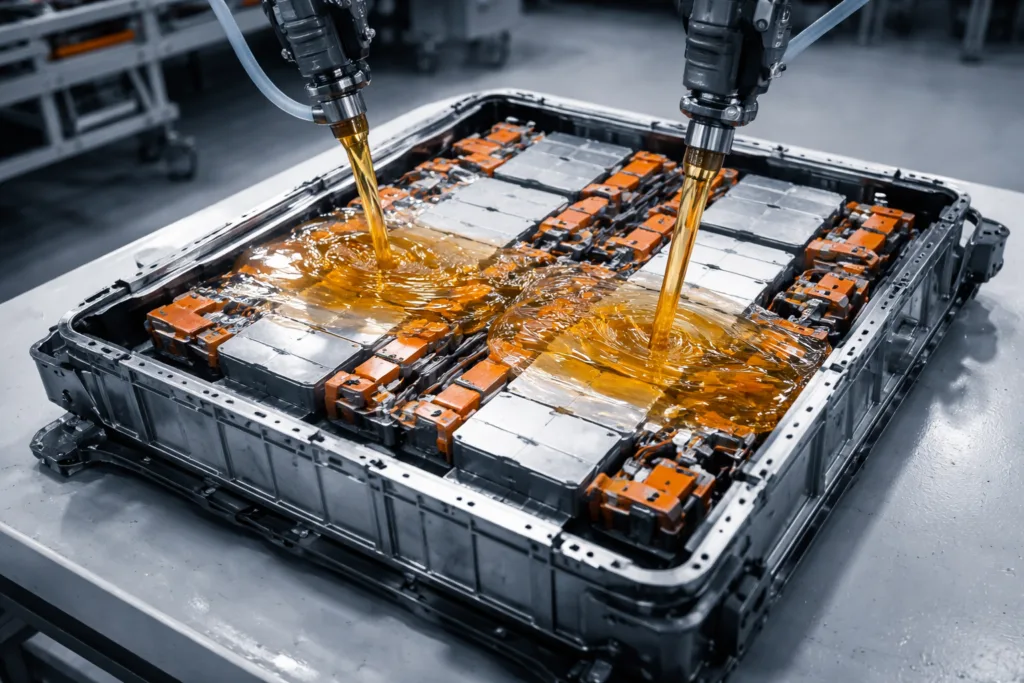
Understanding Structural vs. Thermal Adhesives in CTP Technology
In battery assembly, especially within innovative cell-to-pack (CTP) designs, two adhesive types take center stage: structural adhesives and thermal adhesives. Both impact how battery modules are built, but their roles and performance traits differ sharply. As CTP technology redefines the future of electric vehicles and stationary energy storage, understanding these adhesive choices is crucial for anyone in engineering, manufacturing, or material R&D. This article explores the differences, applications, and real-world innovations shaping modern adhesive use in CTP battery packs.
What is CTP (Cell-to-Pack) Technology?
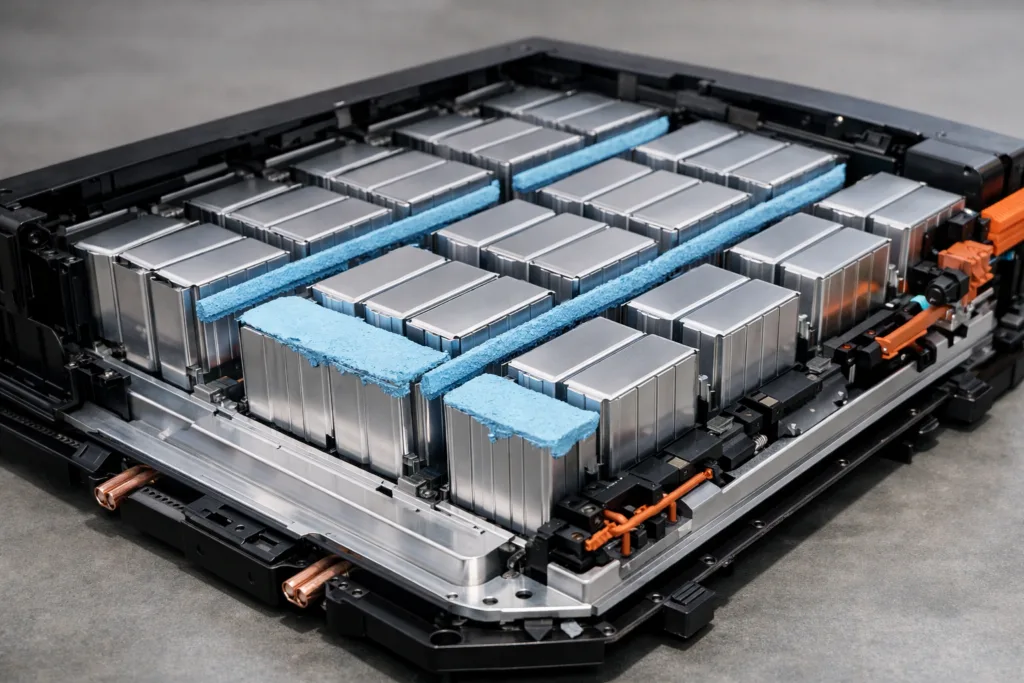
CTP technology means battery cells are directly integrated into the pack without traditional module enclosures. This design boosts energy density, lowers costs, and streamlines assembly, but also raises new challenges for bonding and thermal management—areas where adhesive choice plays a pivotal role.
Why Adhesives Matter in Battery Assembly
Adhesives do more than connect parts—they affect performance, heat dissipation, vibration damping, and the long-term stability of battery systems. Their properties define bonding integrity, resistance to environmental stress, and even the safety profile of energy storage devices.
Structural Adhesives: Backbone of Battery Integrity
Structural adhesives are engineered to bond mechanical components, providing strong, load-bearing joints essential in CTP pack construction. They typically resist shear, peel, and impact forces, holding battery cells and frames together through years of real-world use.
Main Functions and Features
- High-strength bonding for metal, plastic, and composite elements
- Durability against vibration, mechanical stress, and fatigue
- Avoids traditional fasteners—saves weight and assembly time
Common Types of Structural Adhesives
- Epoxy adhesives — known for strong, rigid bonds and excellent chemical resistance. For details on industrial applications, see epoxy adhesive.
- Polyurethane adhesives — provide tough bonds with a hint of flexibility, suited for joining dissimilar substrates prone to expansion. Learn about options at polyurethane structural adhesive.
- Acrylic adhesives — blend speed and strength, ideal for high throughput lines and mixed-material assemblies.
Performance in CTP Designs
In CTP packs, structural adhesives must maintain joint integrity across thermal cycles, swelling/shrinkage from charge-discharge, and operational shocks. Key metrics include lap shear strength, peel resistance, and fixture time. ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, recommends matching adhesive choice to factors like substrate compatibility (aluminum, copper, plastics), bond thickness, open time, and cure mechanism to prevent premature failures such as delamination or joint cracking.
Thermal Adhesives: Managing Heat for Optimal Performance
Thermal adhesives—sometimes called thermal interface materials (TIMs)—prioritize heat transfer and dissipation, especially in areas where battery cell temperatures must stay within tight limits. Their main role: channel heat away from critical areas, protecting cells from overheating and maximizing pack lifespan.
Core Features of Thermal Adhesives
- High thermal conductivity for rapid heat dissipation
- Electrical insulation to prevent short circuits
- Some degree of flexibility for vibration compensation
Examples and Materials Science Advances
- Silicone-based thermal adhesives—offer excellent flexibility and temperature resilience. For advanced choices, refer to polyurethane potting glue with thermal additives.
- Thermally-conductive epoxies and polyurethanes—used to bond and also transfer heat between battery cells and cooling plates.
Recent advances include incorporating ceramic, graphite, or boron nitride fillers to achieve higher thermal conductivities (1–6 W/m·K+). These innovations are vital for the fast-charging demands and high-output profiles of 2026 EV batteries.
Role in CTP Battery Assembly: Practical Insights
Thermal adhesives fulfill dual roles in CTP packs—structural positioning and thermal management. Placement matters: they’re used between cells and pack baseplates, around cooling fins, and in direct contact with heat-sensitive electronics. Manufacturers routinely test performance through thermal cycling, humidity aging, and chemical exposure to ensure long-term reliability and safety.
Key Differences: Structural vs. Thermal Adhesives
| Feature | Structural Adhesives | Thermal Adhesives |
|---|---|---|
| Main Purpose | Mechanical joining | Heat management |
| Typical Location in CTP | Cell-to-frame, frame-to-pack, busbar bonding | Cell-to-cooling plate, electronics interface |
| Required Properties | High shear/peel strength, rigidity | Thermal conductivity, electrical insulation |
| Material Base | Epoxy, polyurethane, acrylic | Silicone, polyurethane, filled epoxy |
| Common Additives | Glass beads, tougheners, adhesion promoters | Ceramic, graphite, BN fillers |
| Failure Mode | Delamination, cracking, poor wetting | Thermal cycling-induced loss of conductivity |
| Cure Profile | Room or elevated temperature, sometimes UV | Room, elevated, or low-exotherm to avoid hot spots |
How Adhesive Selection Shapes Battery Performance
A well-chosen adhesive optimizes pack safety, extends life, and streamlines assembly. Under-performing adhesives—whether structural or thermal—can lead to heat build-up, joint failure, or even catastrophic cell events. Selection comes down to balancing strength, thermal transfer, speed of cure, and ease of application.
Performance Factors to Consider
- Substrate compatibility (metals, polymers, composites)
- Bond-line thickness and cure shrinkage
- Operating temperature and exposure to chemicals/humidity
- Fixture time versus production speed
- Long-term aging, vibration, and fatigue resistance
Real-World Applications: Battery Assembly Case Studies
Modern CTP packs rely on both adhesive types in tandem:
- High-capacity EV packs use toughened epoxies at cell–frame interfaces, paired with thermal greases or potting compounds at cell–baseplate contact points.
- Stationary systems employ polyurethane for vibration damping and silicone for heat spread in high-cycle environments.
- Manufacturers integrate UV-curing adhesives in line for rapid assembly, as seen in recent smart grid battery deployments.
Process Stability and Failure Prevention
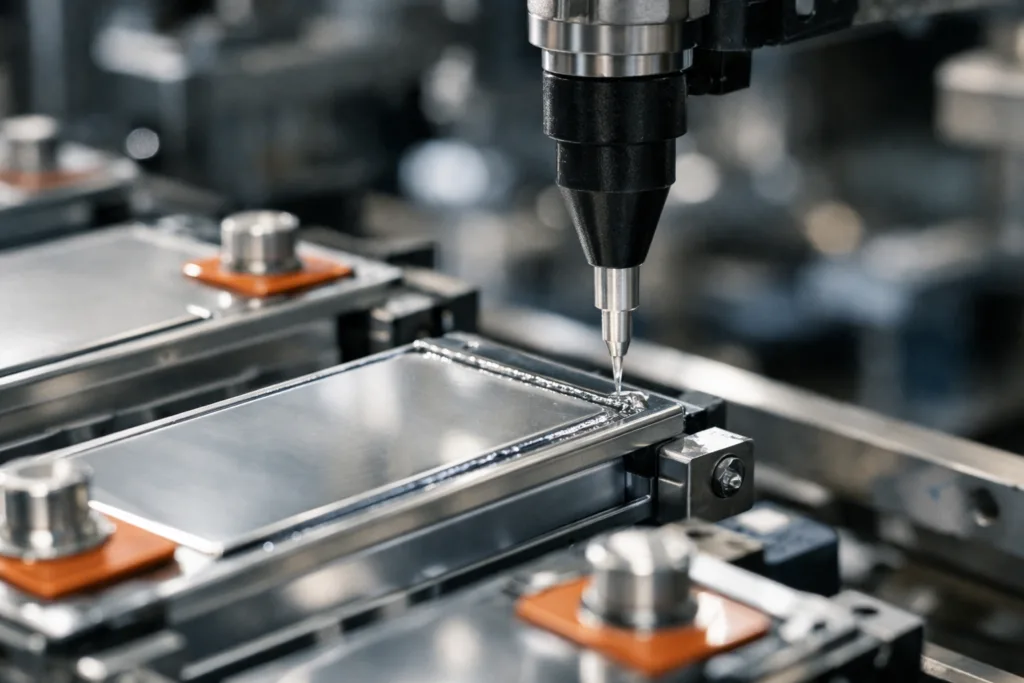
At ZDS Adhesive, engineers prioritize process controls like substrate cleaning, primer selection, and application method (jetting, bead, robotic dispensing) to ensure repeatable bonds. Routine tests include lap shear, peel, and thermal cycling to catch weak points early.
Surface preparation is also vital. For detailed techniques that improve bond strength, consult our surface preparation guide.
Innovations in Adhesive Technology for CTP Packs
Recent materials science advances enable adhesives tailored for CTP demands:
- Fast-curing, two-component formulas for quicker assembly lines
- Hybrid adhesives combining mechanical strength and thermal management
- Low volatile organic compound (VOC) content for safer factory environments
- Built-in flame retardancy and electric insulation for improved safety
Sustainability is also advancing with water-based and recyclable adhesive formulations.
Future Trends: 2026 and Beyond
Looking ahead, adhesives for CTP will likely push toward multi-functionality—being both structural and thermally conductive, self-healing to counter fatigue crack growth, and smart enough to monitor bond health. As battery packs scale to larger formats, these properties become more critical for safety, cost, and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Adhesive for CTP Battery Assembly
In summary, the decision between structural and thermal adhesives in CTP technology is never black-and-white. Successful battery assembly springs from a thoughtful blend of both, chosen for the substrate, load scenario, and thermal environment. Engineers must weigh mechanical integrity, heat management, cure speed, and production realities—always keeping one eye on the latest advancements in adhesive materials science. Making the right choice means safer, more efficient, and longer-lasting battery packs for EVs and beyond.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between structural and thermal adhesives?
Structural adhesives provide mechanical strength for joining parts, while thermal adhesives focus on transferring heat to manage battery temperature.
Can one adhesive act as both structural and thermal in CTP packs?
Some hybrid adhesives offer limited dual functionality, but most applications combine distinct products for best performance in each area.
How do I select the right adhesive for my battery assembly?
Consider substrate type, required bond strength, operating temperature, and cure profile. Always perform compatibility and aging tests before final selection.
Are there adhesives suitable for both high strength and high thermal conductivity?
Recent innovations include hybrid materials that balance strength and conductivity, but standard choices still separate these functions for reliability.
What are common failure modes when using adhesives in CTP packs?
Delamination, heat buildup, cure shrinkage, and poor surface wetting are the main risks. Prevent with proper selection, surface prep, and testing.
How have adhesives for CTP evolved since 2020?
New formulas offer faster curing, higher heat conductivity, improved flame retardancy, and lower VOC emissions, enabling more advanced battery designs.
Related Reading
- How Thermal Adhesives Shape the Future of EV Battery Packs
- Epoxy vs Silicone vs Polyurethane: Industrial Adhesive Selection Simplified
- Avoiding Costly Failures: Guide to Industrial Adhesive Pitfalls
- Step-by-Step: Choosing Your Perfect Industrial Adhesive
- Industrial Adhesives Explained: Types, Uses, and Selection Guide