Introduction: Why Battery Bonding and Repairability Matter in 2026
As electronic devices from smartphones to electric vehicles (EVs) become more powerful and complex, the debate around battery bonding and repairability has moved center stage. “Serviceable vs. Permanent Battery Bonding: Repairability Trends” holds powerful implications for how devices are used, maintained, and eventually recycled. For engineers, designers, and end-users, understanding the pros and cons of these bonding approaches is no longer optional—it’s essential for responsible manufacturing and informed buying in 2026.
Understanding Battery Bonding: The Foundation of Modern Assemblies
Battery bonding refers to the methods and materials used to physically secure batteries within devices. Advanced adhesives, including epoxy adhesives and PUR hot melts, have often replaced mechanical fasteners in pursuit of lighter, sleeker, and more robust assemblies. The choice between serviceable and permanent battery bonding fundamentally shapes the repairability, durability, and environmental footprint of the end product.
Serviceable Battery Bonding: Designed for Repairs
Serviceable bonding uses adhesives or fasteners that allow safe battery removal without damaging surrounding components. This approach often prioritizes:
- Lower adhesive strength (or specially engineered release properties)
- Modular battery packs or trays for easy swap-outs
- Minimal chemical residue and rework risk
Manufacturers using serviceable solutions aim to boost repair rates and extend product lifecycles. For example, in consumer electronics, replaceable battery designs have re-emerged in response to e-waste regulations and right-to-repair movements globally.
Permanently Bonded Batteries: Engineering for Longevity—at a Cost
Permanently bonded batteries are set in place with high-strength adhesives or potting compounds, creating durable seals that resist moisture, shock, and tampering. This technique provides unmatched durability and miniaturization but significantly increases the challenge of battery or component repair. OEMs favor permanent bonding for:
- Ultra-slim smartphone designs
- Water- and dust-proofing in wearables
- High-vibration or EV battery modules
Repairability Trends in Consumer Electronics
Recent years have seen a renewed push for repair-friendly products. Devices with serviceable battery bonds now receive higher repairability scores from advocacy groups and influential review sites. Yet, many phones and tablets still use permanent adhesives, trading off repair for style or sealing performance.
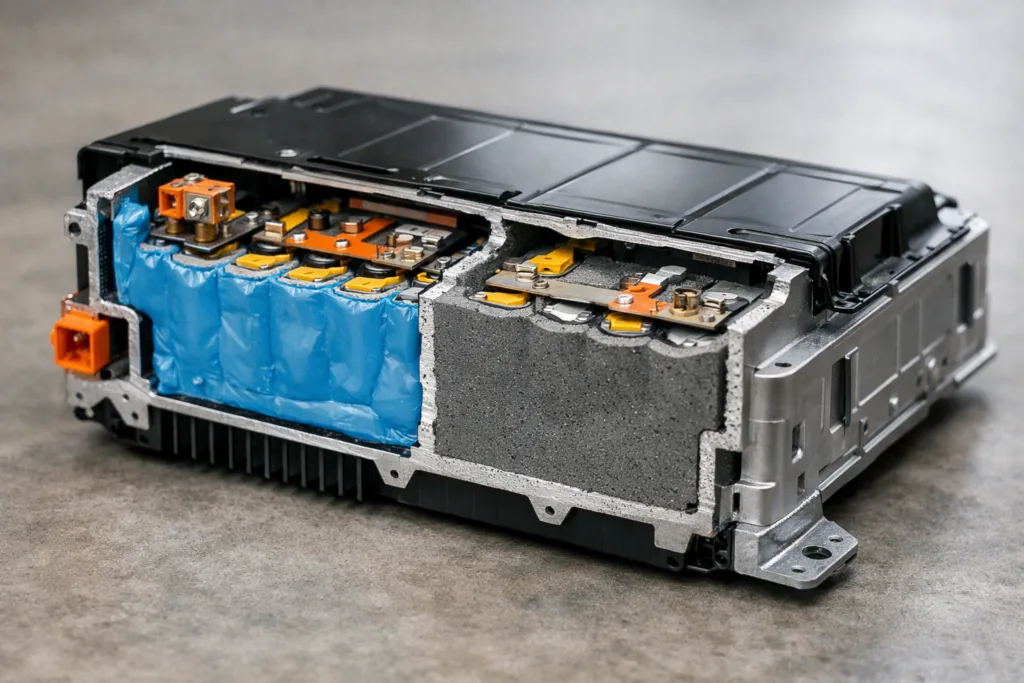
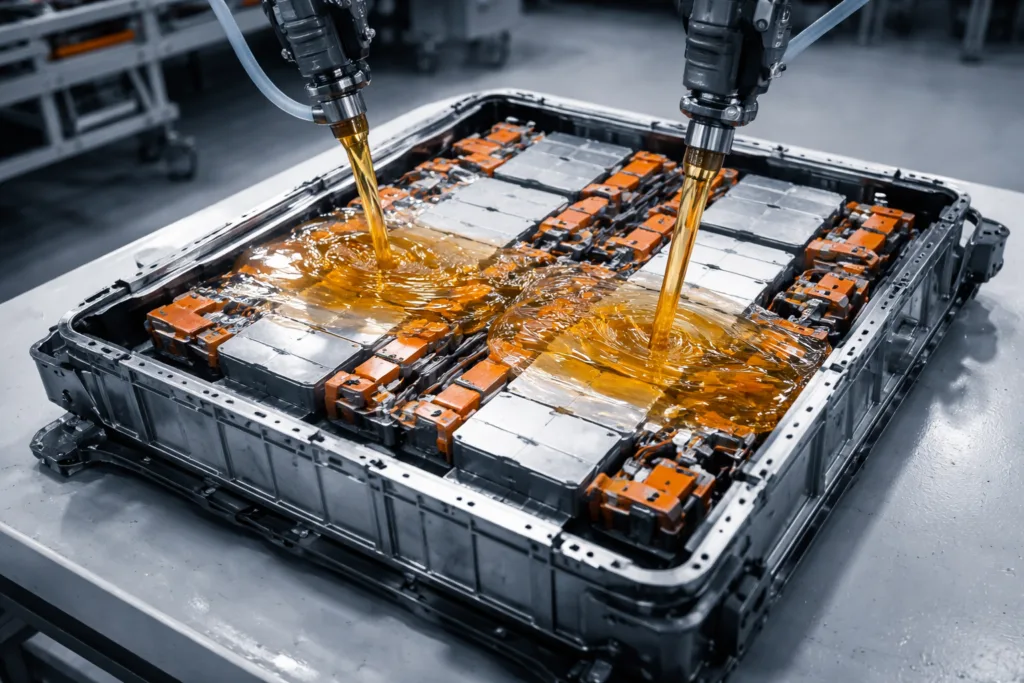
Repairability in Electric Vehicles (EVs): Unique Demands
EV battery packs are heavy, high-voltage, and safety-critical. Bonding solutions must balance service access with structural strength. ZDS Adhesive, an industrial adhesive manufacturer, suggests a decision matrix:
- Accessible module-level designs: Use elastomeric adhesives for shock absorption and future-proofs serviceability
- Permanently sealed modules: Prioritize low water absorption, fire resistance, and chemical endurance
Engineers must decide: is it better to swap out a faulty module, or seal it forever to prevent failures? Regional regulations increasingly require manufacturers to design for dismantling and recycling, making serviceable bonding more popular in major markets.
Battery Bonding Technologies: An Evolving Toolkit
Continuous advances in bonding chemistry are blurring the lines between “serviceable” and “permanent.” Hybrid adhesives now offer both strong bonds and the ability to be released under specific conditions (e.g., heat, solvents, UV exposure). These enable selective disassembly without sacrificing on-field performance.
- Epoxy with low glass transition temperature (Tg) enables rework without splitting the case
- Dual-cure acrylics provide initial tack and later high final strength
- Hot-melt and low-residue tapes support both fast assembly and clean repair
Comparison Table: Serviceable vs. Permanent Battery Bonding in 2026
| Aspect | Serviceable Bonding | Permanently Bonded |
|---|---|---|
| Repairability | High—can replace battery without damage | Low—special tools and training needed |
| Structural Integrity | Moderate—suitable for most devices | High—ideal for harsh environments |
| Sealing/Protection | Basic moisture/dust protection | Excellent water/chemical resistance |
| Sustainability Potential | Strong—supports extended lifecycle | Lower—hard to disassemble/recycle |
| Assembly Speed | Fast—less complex tooling | Slower—fewer opportunities for error correction |
How Bonding Choices Impact Product Lifecycle and E-Waste
A serviceable battery bond often extends the useful life of a device by enabling repair and upgrades. Environmentally, this reduces hazardous waste and supports circular economy goals. In contrast, a non-removable bond often sends the entire product to landfill when a single part fails.
User Experience: Serviceable Bonds or Sealed Permanence?
There is a direct trade-off: users want slim, rugged, high-performance gadgets, but also transparent, affordable repairs. Some brands are surveying customers to adjust future designs, with users increasingly willing to accept a slightly thicker device if it means easy battery swaps down the road.
Case Study: Battery Bonding in Smartphones
Many 2024–2026 flagship phones have moved from edge-to-edge glue to more accessible bonding lines or partial tab adhesives. This shift, driven by consumer demand for repairability as well as new regulations, allows independent shops to perform faster, less destructive battery replacements.
Case Study: Battery Bonding in Electric Vehicles
By 2026, large EV manufacturers are piloting semi-serviceable battery packs held by engineered PUR or polyurethane structural adhesives. This strategy enables selective replacement of faulty modules without scrapping the whole pack, cutting costs and waste.
Sustainability and Regulatory Trends: Repairability on the Agenda
Global directives—especially in the EU and some U.S. states—now compel electronics and automotive brands to enable easier battery service and end-of-life recycling. Manufacturers are redesigning adhesives for proven disassembly processes using heat, low-toxicity solvents, or ultrasonic tools.
When Permanent Bonding is Still Essential
Some applications—medical implants, ruggedized field devices, certain EV power modules—require permanent battery bonds for anti-tamper, vibration, or extreme environmental protection. In these contexts, repairability must yield to reliability and safety demands.
Real-World Engineering Guidance: Choosing Based on Requirement
From an assembly-line viewpoint at ZDS Adhesive, certain rules of thumb apply:
- Use serviceable bonds in low-stress, consumer-facing, and regulated-repair markets
- Choose permanent options when waterproofing, miniaturization, or security are non-negotiable
- Incorporate hybrid adhesives if you need both strength and future disassembly
Proper surface prep is always critical; release performance is determined by initial wetting, substrate energy, and cure profiles—a lesson reinforced by decades of industrial adhesive testing.
Battery Bonding Failure Modes: Risks for Each Method
Serviceable adhesives run the risk of creep or bond breakage under high load, especially if process controls are loose. Permanent adhesives are nearly impossible to remove without damage, and often mask developing issues, complicating diagnostics and root-cause analysis. Choose wisely based on real-world use cases.
Environmental Impact: Balancing Repair, Recycling, and Waste
Battery bonding chemistry plays a subtle but crucial role in device recycling. Potting compounds with hazardous additives complicate recycling; meanwhile, clean-release adhesives support greener EOL (end-of-life) processing. Brands moving toward serviceable bonds may gain market share based on sustainability claims.
Trends in Battery Bonding for 2026 and Beyond
Flagship trends on the horizon include:
- Smart adhesives with on-command release (e.g., activated by radiofrequency or light)
- Modular battery packs for both phones and vehicles
- Full digital traceability of bond process, aiding future repair, warranty, and recycling
Manufacturers are increasingly specifying adhesive types at the design phase, not as an afterthought—integrating repair and recycling goals early for compliance and differentiation.
How to Specify the Right Battery Bonding Method
Project managers and engineers must consider:
- Product function (ruggedness, mobility, thermal exposure)
- Regulatory landscape (regional eco-label rules, recycling mandates)
- Service plan (authorized repair network vs. open repairability)
- End-of-life strategy (component harvest, disassembly feasibility)
Key Takeaways: Serviceable vs. Permanent Bonding for Repairability
Decisions about battery bonding are never one-size-fits-all. However, current repairability trends strongly favor serviceable adhesives and joint designs wherever possible—without sacrificing device protection and reliability. Both manufacturers and end-users benefit from more transparent, modular, and repair-friendly battery attachment systems.
Serviceable vs. Permanent Battery Bonding: Repairability Trends
The debate between serviceable and permanent battery bonding is more than just a manufacturing choice; it is central to product lifecycle, repair culture, and environmental stewardship. As technology matures, stakeholder expectations are refocusing on designs that prioritize repair without a loss of durability—or vice versa, depending on application constraints.
Conclusion: Repairability’s Bright Future in Battery Bonding
Battery bonding shapes almost every modern device’s lifecycle. In 2026, customer expectation, environmental regulation, and technological innovation are converging to make repairability a design requirement—not an afterthought. Serviceable bonds make for happier, longer-lasting products, while permanent bonds retain their place in the toughest applications. The smartest engineers—and the world’s most satisfied users—will choose purposely, trading cost, performance, and sustainability with clear eyes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is serviceable battery bonding?
Serviceable battery bonding uses adhesives or methods that allow batteries to be replaced or repaired without damaging the device, extending its usable life.
Why do some devices use permanent battery bonding?
Permanent bonding offers extra durability, water resistance, or size reduction but makes repairs or recycling more difficult or costly.
How does battery bonding affect sustainability?
Serviceable batteries reduce e-waste by prolonging device life, while permanent bonds often lead to more devices being discarded instead of repaired.
Can repairability be improved without sacrificing device performance?
Yes. New hybrid bonding technologies enable strong adhesive performance that can still be safely released for authorized repairs when needed.
What types of adhesives are commonly used for battery bonding?
Common types include epoxies, polyurethane, hot-melt, and specialty tapes; selection depends on strength, reworkability, and environmental needs.
Are serviceable battery bonds becoming more common in 2026?
Yes. Due to regulations and consumer demand, more devices now feature repairable bonding solutions, especially in Europe and North America.
Related Reading
- 10 Factors for Reliable EV Battery Cooling Plate Adhesives
- Breakthroughs in Foldable Phone Hinge Adhesives Explained
- Silicone vs. Polyurethane: Potting Battery Modules Pros & Cons
- Understanding Structural vs. Thermal Adhesives for CTP Battery Innovation
- Preventing Thermal Runaway: How UL94 V-0 Solutions Safeguard Batteries